Analysis of the Sequence Preference of Saporin by Deep Sequencing
- PMID: 35969718
- PMCID: PMC9486812
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.2c00531
Analysis of the Sequence Preference of Saporin by Deep Sequencing
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Analysis of the Sequence Preference of Saporin by Deep Sequencing".ACS Chem Biol. 2024 Feb 16;19(2):584-585. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.3c00733. Epub 2024 Jan 22. ACS Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38258295 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
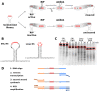
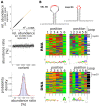
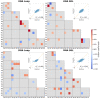
Ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) are RNA:adenosine glycosidases that inactivate eukaryotic ribosomes by depurinating the sarcin-ricin loop (SRL) in 28S rRNA. The GAGA sequence at the top of the SRL or at the top of a hairpin loop is assumed to be their target motif. Saporin is a RIP widely used to develop immunotoxins for research and medical applications, but its sequence specificity has not been investigated. Here, we combine the conventional aniline cleavage assay for depurinated nucleic acids with high-throughput sequencing to study sequence-specific depurination of oligonucleotides caused by saporin. Our data reveal the sequence preference of saporin for different substrates and show that the GAGA motif is not efficiently targeted by this protein, neither in RNA nor in DNA. Instead, a preference of saporin for certain hairpin DNAs was observed. The observed sequence-specific activity of saporin may be relevant to antiviral or apoptosis-inducing effects of RIPs. The developed method could also be useful for studying the sequence specificity of depurination by other RIPs or enzymes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Polynucleotide:adenosine glycosidase activity of saporin-L1: effect on various forms of mammalian DNA.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Jul 14;1480(1-2):258-66. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4838(00)00077-7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10899626
-
Transition state analogues rescue ribosomes from saporin-L1 ribosome inactivating protein.Biochemistry. 2009 Oct 20;48(41):9941-8. doi: 10.1021/bi901425h. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19764816 Free PMC article.
-
Polynucleotide: adenosine glycosidase activity of saporin-L1: effect on DNA, RNA and poly(A).Biochem J. 1996 Oct 15;319 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):507-13. doi: 10.1042/bj3190507. Biochem J. 1996. PMID: 8912688 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ricin to the ribosome.Toxicon. 2013 Jul;69:143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Toxicon. 2013. PMID: 23454625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structures of eukaryotic ribosomal stalk proteins and its complex with trichosanthin, and their implications in recruiting ribosome-inactivating proteins to the ribosomes.Toxins (Basel). 2015 Feb 25;7(3):638-47. doi: 10.3390/toxins7030638. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 25723321 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid Enzymatic Detection of Shiga-Toxin-Producing E. coli Using Fluorescence-Labeled Oligonucleotide Substrates.ACS Infect Dis. 2024 Dec 13;10(12):4103-4114. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00221. Epub 2024 Nov 22. ACS Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39576816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Endo Y.; Mitsui K.; Motizuki M.; Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 5908–5912. 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)45660-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Montanaro L.; Sperti S.; Mattioli A.; Testoni G.; Stirpe F. Inhibition by ricin of protein synthesis in vitro. Inhibition of the binding of elongation factor 2 and of adenosine diphosphate-ribosylated elongation factor 2 to ribosomes. Biochem. J. 1975, 146, 127–131. 10.1042/bj1460127. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

