Inferring gene regulation from stochastic transcriptional variation across single cells at steady state
- PMID: 35969771
- PMCID: PMC9407670
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2207392119
Inferring gene regulation from stochastic transcriptional variation across single cells at steady state
Abstract
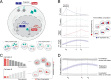
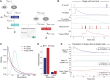
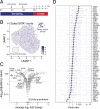
Regulatory relationships between transcription factors (TFs) and their target genes lie at the heart of cellular identity and function; however, uncovering these relationships is often labor-intensive and requires perturbations. Here, we propose a principled framework to systematically infer gene regulation for all TFs simultaneously in cells at steady state by leveraging the intrinsic variation in the transcriptional abundance across single cells. Through modeling and simulations, we characterize how transcriptional bursts of a TF gene are propagated to its target genes, including the expected ranges of time delay and magnitude of maximum covariation. We distinguish these temporal trends from the time-invariant covariation arising from cell states, and we delineate the experimental and technical requirements for leveraging these small but meaningful cofluctuations in the presence of measurement noise. While current technology does not yet allow adequate power for definitively detecting regulatory relationships for all TFs simultaneously in cells at steady state, we investigate a small-scale dataset to inform future experimental design. This study supports the potential value of mapping regulatory connections through stochastic variation, and it motivates further technological development to achieve its full potential.
Keywords: gene regulation; single-cell transcriptomics; transcriptional bursting.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: In advance of review, the authors noted that one of the authors (E.S.L.) and one of the reviewers (A.v.O.) were both among more than 80 coauthors on a community white paper describing plans for a Human Cell Atlas that was posted on eLife in December 2017 (
Figures

References
-
- Butte A. J., Kohane I. S., Mutual information relevance networks: Functional genomic clustering using pairwise entropy measurements. Pac. Symp. Biocomput. 2000, 418–429 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Carter S. L., Brechbühler C. M., Griffin M., Bond A. T., Gene co-expression network topology provides a framework for molecular characterization of cellular state. Bioinformatics 20, 2242–2250 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Stuart J. M., Segal E., Koller D., Kim S. K., A gene-coexpression network for global discovery of conserved genetic modules. Science 302, 249–255 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Zhang B., Horvath S., A general framework for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 4, 17 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Hu Z., Killion P. J., Iyer V. R., Genetic reconstruction of a functional transcriptional regulatory network. Nat. Genet. 39, 683–687 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

