Structure of a cholinergic cell membrane
- PMID: 35969788
- PMCID: PMC9407305
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2207641119
Structure of a cholinergic cell membrane
Abstract
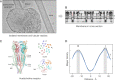
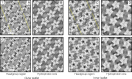
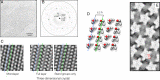
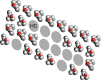
Cell membranes are complex assemblies of proteins and lipids making transient or long-term associations that have yet to be characterized at a molecular level. Here, cryo-electron microscopy is applied to determine how phospholipids and cholesterol arrange between neighboring proteins (nicotinic acetylcholine receptors) of Torpedo cholinergic membrane. The lipids exhibit distinct properties in the two leaflets of the bilayer, influenced by the protein surfaces and by differences in cholesterol concentration. In the outer leaflet, the lipids show no consistent motif away from the protein surfaces, in keeping with their assumed fluidity. In the inner leaflet, where the cholesterol concentration is higher, the lipids organize into extensive close-packed linear arrays. These arrays are built from the sterol groups of cholesterol and the initial saturated portions of the phospholipid hydrocarbon chains. Together, they create an ordered ∼7 Å-thick "skin" within the hydrophobic core of the bilayer. The packing of lipids in the arrays appears to bear a close relationship to the linear cholesterol arrays that form crystalline monolayers at the air-water interface.
Keywords: acetylcholine receptor; cholesterol; cryo-EM; lipid bilayer; phospholipid.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L., The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science 175, 720–731 (1972). - PubMed
-
- Gennis R. B., Biomembranes: Molecular Structure and Function (Springer-Verlag New York Inc., 1989).
-
- Bretscher M. S., Asymmetrical lipid bilayer structure for biological membranes. Nat. New Biol. 236, 11–12 (1972). - PubMed
-
- Levine Y. K., Wilkins M. H. F., Structure of oriented lipid bilayers. Nat. New Biol. 230, 69–72 (1971). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

