Relapse and Remission in Children With Chronic Noninfectious Uveitis Treated With Methotrexate
- PMID: 35970521
- PMCID: PMC10151125
- DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.220007
Relapse and Remission in Children With Chronic Noninfectious Uveitis Treated With Methotrexate
Conflict of interest statement
SY is a consultant for Santen and Clearside Biomedical, unrelated to this study. KARS is a consultant for Accordant, unrelated to this study. SP serves on the Macrophage Activation Syndrome Adjudication Committee for Novartis and is a Doximity Op-Med Fellow for 2021–22, unrelated to this study. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
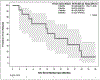
Figures
References
-
- Simonini G, Bracaglia C, Cattalini M, et al. Predictors of relapse after discontinuing systemic treatment in childhood autoimmune chronic uveitis. J Rheumatol 2017;44:822–6. - PubMed
-
- Kalinina Ayuso V, van de Winkel EL, Rothova A, de Boer JH. Relapse rate of uveitis post-methotrexate treatment in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Am J Ophthalmol 2011;151:217–22. - PubMed
-
- Saboo US, Metzinger JL, Radwan A, et al. Risk factors associated with the relapse of uveitis in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a preliminary report. J AAPOS 2013;17:460–4. - PubMed
-
- Acharya NR, Ebert CD, Kelly NK, et al. Discontinuing adalimumab in patients with controlled juvenile idiopathic arthritis-associated uveitis (ADJUST-Adalimumab in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis-associated Uveitis Stopping Trial): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2020;21:887. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources