A GLP1 receptor agonist diabetes drug ameliorates neurodegeneration in a mouse model of infantile neurometabolic disease
- PMID: 35970890
- PMCID: PMC9378686
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-17338-1
A GLP1 receptor agonist diabetes drug ameliorates neurodegeneration in a mouse model of infantile neurometabolic disease
Abstract
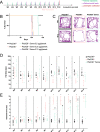
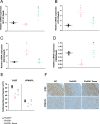
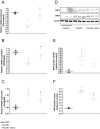
Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (INAD) is a rare paediatric neurodegenerative condition caused by mutations in the PLA2G6 gene, which is also the causative gene for PARK14-linked young adult-onset dystonia parkinsonism. INAD patients usually die within their first decade of life, and there are currently no effective treatments available. GLP1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists are licensed for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus but have also demonstrated neuroprotective properties in a clinical trial for Parkinson's disease. Therefore, we evaluated the therapeutic efficacy of a new recently licensed GLP-1R agonist diabetes drug in a mouse model of INAD. Systemically administered high-dose semaglutide delivered weekly to juvenile INAD mice improved locomotor function and extended the lifespan. An investigation into the mechanisms underlying these therapeutic effects revealed that semaglutide significantly increased levels of key neuroprotective molecules while decreasing those involved in pro-neurodegenerative pathways. The expression of mediators in both the apoptotic and necroptotic pathways were also significantly reduced in semaglutide treated mice. A reduction of neuronal loss and neuroinflammation was observed. Finally, there was no obvious inflammatory response in wild-type mice associated with the repeated high doses of semaglutide used in this study.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Catalytic function of PLA2G6 is impaired by mutations associated with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy but not dystonia-parkinsonism.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 23;5(9):e12897. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012897. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20886109 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Analysis of PLA2G6 in 22 Indian Families with Infantile Neuroaxonal Dystrophy, Atypical Late-Onset Neuroaxonal Dystrophy and Dystonia Parkinsonism Complex.PLoS One. 2016 May 19;11(5):e0155605. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155605. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27196560 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring therapeutic strategies for infantile neuronal axonal dystrophy (INAD/PARK14).Elife. 2023 Jan 16;12:e82555. doi: 10.7554/eLife.82555. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36645408 Free PMC article.
-
PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration in four different populations-case series and literature review.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2022 Aug;101:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2022.06.016. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2022. PMID: 35803092 Review.
-
Mouse models of human INAD by Pla2g6 deficiency.Histol Histopathol. 2013 Aug;28(8):965-9. doi: 10.14670/HH-28.965. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Histol Histopathol. 2013. PMID: 23467909 Review.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of Semaglutide's Influence on Cognitive Function in Preclinical Animal Models and Cell-Line Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 2;25(9):4972. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094972. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732190 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype-Phenotype Relations for the Dystonia-Parkinsonism Genes GLB1, SLC6A3, SLC30A10, SLC39A14, and PLA2G6: MDSGene Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 25;26(9):4074. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094074. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362326 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Trajectories Towards Possible Effects of Semaglutide for Amelioration of Reserpine-induced Fibromyalgia in Rats: Contribution of cAMP/PKA/p-CREB and M1/M2 Microglia Polarization.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 17;20(1):43. doi: 10.1007/s11481-025-10196-4. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40240584 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of semaglutide and liraglutide as a therapeutic option for obesity.Front Nutr. 2024 Apr 29;11:1398059. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1398059. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38742021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Impact of Semaglutide on Cognitive Function and Anxiety-Related Behaviors in a Murine Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Biomedicines. 2024 Nov 25;12(12):2689. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122689. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gregory, A., Kurian, M. A., Maher, E. R., Hogarth, P. & Hayflick, S. J. in GeneReviews((R)) (eds M. P. Adam et al.) (1993).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

