Dehydration Tolerance in Epidemic versus Nonepidemic MRSA Demonstrated by Isothermal Microcalorimetry
- PMID: 35972129
- PMCID: PMC9602581
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00615-22
Dehydration Tolerance in Epidemic versus Nonepidemic MRSA Demonstrated by Isothermal Microcalorimetry
Abstract
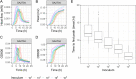
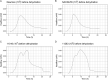
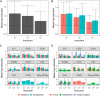
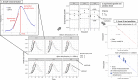
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) clusters are considered epidemic or nonepidemic based on their ability to spread effectively. Successful transmission could be influenced by dehydration tolerance. Current methods for determination of dehydration tolerance lack accuracy. Here, a climate-controlled in vitro dehydration assay using isothermal microcalorimetry (IMC) was developed and linked with mathematical modeling to determine survival of 44 epidemic versus 54 nonepidemic MRSA strains from France, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands after 1 week of dehydration. For each MRSA strain, the growth parameters time to end of first growth phase (tmax [h]) and maximal exponential growth rate (μm) were deduced from IMC data for 3 experimental replicates, 3 different starting inocula, and before and after dehydration. If the maximal exponential growth rate was within predefined margins (±36% of the mean), a linear relationship between tmax and starting inoculum could be utilized to predict log reduction after dehydration for individual strains. With these criteria, 1,330 of 1,764 heat flow curves (data sets) (75%) could be analyzed to calculate the post-dehydration inoculum size, and thus the log reduction due to dehydration, for 90 of 98 strains (92%). Overall reduction was ~1 log after 1 week. No difference in dehydration tolerance was found between the epidemic and nonepidemic strains. Log reduction was negatively correlated with starting inoculum, indicating better survival of higher inocula. This study presents a framework to quantify bacterial survival. MRSA strains showed great capacity to persist in the environment, irrespective of epidemiological success. This finding strengthens the need for effective surface cleaning to contain MRSA transmission. IMPORTANCE Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a major cause of infections globally. While some MRSA clusters have spread worldwide, others are not able to disseminate successfully beyond certain regions despite frequent introduction. Dehydration tolerance facilitates transmission in hospital environments through enhanced survival on surfaces and fomites, potentially explaining differences in transmission success between MRSA clusters. Unfortunately, the currently available techniques to determine dehydration tolerance of cluster-forming bacteria like S. aureus are labor-intensive and unreliable due to their dependence on quantitative culturing. In this study, bacterial survival was assessed in a newly developed assay using isothermal microcalorimetry. With this technique, the effect of drying can be determined without the disadvantages of quantitative culturing. In combination with a newly developed mathematical algorithm, we determined dehydration tolerance of a large number of MRSA strains in a systematic, unbiased, and robust manner.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; desiccation; environmental survival; epidemiological success; transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Harkins CP, Pichon B, Doumith M, Parkhill J, Westh H, Tomasz A, de Lencastre H, Bentley SD, Kearns AM, Holden MTG. 2017. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus emerged long before the introduction of methicillin into clinical practice. Genome Biol 18:130. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1252-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

