[Effectiveness of mirror therapy and action observation therapy in infantile cerebral palsy: a systematic review]
- PMID: 35972309
- PMCID: PMC10130800
- DOI: 10.23938/ASSN.1003
[Effectiveness of mirror therapy and action observation therapy in infantile cerebral palsy: a systematic review]
Abstract
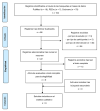
The aim of this review was to assess the effectiveness of mirror therapy (MT) and action observation therapy (AOT) on upper limb-related body structures, body functions, activity, and involvement in patients with infantile cerebral palsy (ICP). We carried out a systematic review of randomized controlled trials published over the past 10 years, in which MT or AOT was compared to other ICP-directed interventions. Nine studies met the inclusion criteria and we measured their methodological quality using the PEDro scale. MT or AOT seem to significantly improve upper limb-related body structures, body function, activity, and participation in comparison to other interventions for ICP. Both seem to improve overall quality of life, reduce their disability, and promote its functioning. Further studies with higher methodological quality need to be developed to confirm the long-term effectiveness of MT and AOT.
El objetivo de esta revisión fue evaluar la eficacia de la terapia en espejo (TE) y terapia de observación de acciones (AOT) en estructuras y funciones corporales, actividad y participación, relacionadas con miembro superior en parálisis cerebral infantil (PCI). Se realizó una revisión sistemática de ensayos controlados aleatorizados publicados en los últimos diez años, que investigaran TE o AOT frente a otras intervenciones en PCI. La calidad metodológica de los nueve estudios incluidos se evaluó con la escala PEDro. El tratamiento con TE o AOT parece mostrar mejoras significativas en estructuras y funciones corporales, actividades y participación del miembro superior comparado con otras intervenciones en PCI. Ambas intervenciones parecen mejorar la calidad de vida al abarcar la globalidad del paciente, reducir la discapacidad y favorecer su funcionamiento. Se necesitan más estudios con mayor calidad metodológica para respaldar estas intervenciones a largo plazo.
Conflict of interest statement
References
-
- 1. Novak I, Morgan C, Adde L, Blackman J, Boyd RN, Brunstrom-Hernandez J, et al. Early, accurate diagnosis and early intervention in cerebral palsy: advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA Pediatr 2017; 171: 897-907. Doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.1689 - PMC - PubMed
- Novak I, Morgan C, Adde L, Blackman J, Boyd RN, Brunstrom-Hernandez J, et al. Early, accurate diagnosis and early intervention in cerebral palsy: advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171:897–907. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.1689. - DOI - PMC - PubMed