Real-world experience with ruxolitinib for steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: a single center experience
- PMID: 35972605
- PMCID: PMC9668796
- DOI: 10.1007/s12185-022-03434-5
Real-world experience with ruxolitinib for steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: a single center experience
Abstract
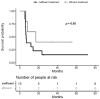
Steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease (SR-aGVHD) remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). Ruxolitinib (RUX), an oral JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor, has recently been approved for patients with SR-aGVHD. The aim of this study was to evaluate RUX efficacy and toxicity in a real-world setting. Eighteen patients received RUX at 5 mg or 10 mg twice a day after a median 3 lines of prior unsuccessful immunosuppressive therapy. Median time on RUX therapy was 28 days (range 7-129). Five patients (28%) responded to RUX, including 4 complete responses and 1 partial response. Response to RUX was irrespective of aGVHD grade and the number of involved organs. One-year overall survival (OS) was 60% for RUX-responders versus 31% for non-responders (p = ns). Treatment duration greater than 29.5 days was found to have a positive impact on OS (p < 0.007). Major adverse events during RUX treatment were grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia (61% of patients) and cytomegalovirus reactivation (50%). After median follow-up of 55 days (range 29-706), 14 patients (78%) died, mainly due to further progression of GVHD. RUX may represent a valuable therapeutic option for some patients with advanced SR-aGVHD, but more studies are warranted.
Keywords: Acute graft-versus-host disease; Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Corticosteroids; Refractoriness; Ruxolitinib.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
GH, AS received a speaker honorarium from Novartis. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent advances in acute gastrointestinal graft versus host disease (aGvHD): aspects of steroid-resistant disease.Ann Hematol. 2025 Feb;104(2):855-865. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05952-0. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Ann Hematol. 2025. PMID: 39207560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of steroid-refractory acute/chronic graft versus host disease: A single-center real-world experience of ruxolitinib in combination with extracorporeal photopheresis in a high-risk population.Leuk Res. 2024 Dec;147:107611. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2024.107611. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Leuk Res. 2024. PMID: 39500129
-
The role of ruxolitinib in the management of acute GVHD.Transfus Apher Sci. 2025 Feb;64(1):104055. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2024.104055. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Transfus Apher Sci. 2025. PMID: 39719750
-
Ruxolitinib for pediatric acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease: a single-center retrospective study of efficacy and safety.Ann Hematol. 2025 Jan;104(1):753-760. doi: 10.1007/s00277-025-06225-0. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Ann Hematol. 2025. PMID: 39903278 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib for steroid-refractory graft-versus-host disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised and non-randomised studies.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 29;17(7):e0271979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271979. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35905125 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Basiliximab Treatment for Patients With Steroid-Refractory Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease Following Matched Sibling Donor Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Cell Transplant. 2024 Jan-Dec;33:9636897241257568. doi: 10.1177/09636897241257568. Cell Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38832653 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Manifestations and Prognosis of Chronic Kidney Disease after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2025 Mar 12;11(1):195-205. doi: 10.1159/000545198. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40248133 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in acute gastrointestinal graft versus host disease (aGvHD): aspects of steroid-resistant disease.Ann Hematol. 2025 Feb;104(2):855-865. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05952-0. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Ann Hematol. 2025. PMID: 39207560 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Van Bekkum D, Vos O, Weyzen WW. The pathogenesis of the secondary disease after foreign bone marrow transplantation in x-irradiated mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959;23:75–89. - PubMed
-
- Martin PJ, Rizzo JD, Wingard JR, Ballen K, Curtin PT, Cutler C, et al. First- and second-line systemic treatment of acute graft-versus-host-disease: recommendations of the American Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2012;18:1150–1163. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2012.04.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous