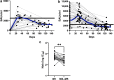
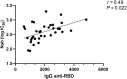
A rapid decline in the anti-receptor-binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein IgG titer in kidney transplant recipients after tixagevimab-cilgavimab administration
- PMID: 35973595
- PMCID: PMC9375643
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.022
A rapid decline in the anti-receptor-binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein IgG titer in kidney transplant recipients after tixagevimab-cilgavimab administration
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

