Effect of chronic stress on tumorigenesis and development
- PMID: 35974132
- PMCID: PMC11071880
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-022-04455-3
Effect of chronic stress on tumorigenesis and development
Abstract
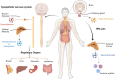
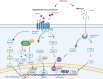
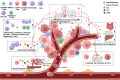
Chronic stress activates the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis to aggravates tumorigenesis and development. Although the importance of SNS and HPA in maintaining homeostasis has already attracted much attention, there is still a lot remained unknown about the molecular mechanisms by which chronic stress influence the occurrence and development of tumor. While some researches have already concluded the mechanisms underlying the effect of chronic stress on tumor, complicated processes of tumor progression resulted in effects of chronic stress on various stages of tumor remains elusive. In this reviews we concluded recent research progresses of chronic stress and its effects on premalignancy, tumorigenesis and tumor development, we comprehensively summarized the molecular mechanisms in between. And we highlight the available treatments and potential therapies for stressed patients with tumor.
Keywords: Epinephrine; Glucocorticoids; Norepinephrine; Tumor formation; Tumor inhibition; Tumor progression.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of stress on the development of psoriasis.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2020 Apr;45(3):284-288. doi: 10.1111/ced.14105. Epub 2019 Oct 8. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31592542 Review.
-
Neuroendocrine coordination and youth behavior problems: A review of studies assessing sympathetic nervous system and hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal axis activity using salivary alpha amylase and salivary cortisol.Horm Behav. 2020 Jun;122:104750. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2020.104750. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Horm Behav. 2020. PMID: 32302595 Review.
-
Pituitary-adrenal and sympathetic nervous system responses to stress in women remitted from recurrent major depression.Psychosom Med. 2008 May;70(4):461-7. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e31816b1aaa. Epub 2008 Mar 31. Psychosom Med. 2008. PMID: 18378864
-
Cancer and stress: NextGen strategies.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Mar;93:368-383. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.11.005. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 33160090 Review.
-
Stress and cancer: The mechanisms of immune dysregulation and management.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 5;13:1032294. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1032294. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275706 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the crosstalk between chronic stress and immune cells: implications for enhanced cancer therapy.Front Neurosci. 2023 Nov 28;17:1321176. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1321176. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38089966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ganoderma lucidum spore oil alleviates psychological stress-evoked tumor progression by enhancing FcγR-mediated macrophage phagocytosis.Chin Med. 2025 Jul 14;20(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01168-0. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40660309 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic stimulation desensitizes β2-adrenergic receptor responses in natural killer cells.Eur J Immunol. 2024 Dec;54(12):e2451299. doi: 10.1002/eji.202451299. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Eur J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39350450 Free PMC article.
-
Stress regulatory hormones and cancer: the contribution of epinephrine and cancer therapeutic value of beta blockers.Endocrine. 2025 May;88(2):359-386. doi: 10.1007/s12020-025-04161-7. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Endocrine. 2025. PMID: 39869294 Review.
-
Stress-induced epinephrine promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the USP10-PLAGL2 signaling loop.Exp Mol Med. 2024 May;56(5):1150-1163. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01223-0. Epub 2024 May 1. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38689092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Article R. Invited minireview: Stress-induced remodeling of lymphoid innervation. Bone. 2008;23:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2007.06.011.Invited. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

