Integrative analysis of transcriptome and metabolome reveals flavonoid biosynthesis regulation in Rhododendron pulchrum petals
- PMID: 35974307
- PMCID: PMC9380304
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-022-03762-y
Integrative analysis of transcriptome and metabolome reveals flavonoid biosynthesis regulation in Rhododendron pulchrum petals
Abstract
Background: Color is the major ornamental feature of the Rhododendron genus, and it is related to the contents of flavonoid in petals. However, the regulatory mechanism of flavonoid biosynthesis in Rhododendron pulchrum remains unknown. The transcriptome and metabolome analysis of Rhododendron pulchrum with white, pink and purple color in this study aimed to reveal the mechanism of flavonoid biosynthesis and to provide insight for improving the petal color.
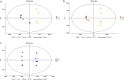
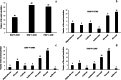
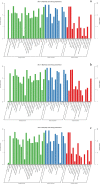
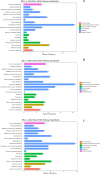
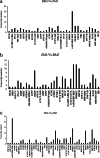
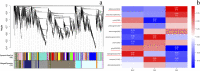
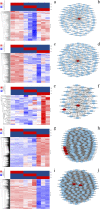
Results: Flavonoids and flavonols are the major components of flavonoid metabolites in R.pulchrum, such as laricitrin, apigenin, tricin, luteolin, isoorientin, isoscutellarein, diosmetin and their glycosides derivatives. With transcriptome and metabolome analysis, we found CHS, FLS, F3'H, F3'5'H, DFR, ANS, GT, FNS, IFR and FAOMT genes showed significantly differential expression in cultivar 'Zihe'. FNS and IFR were discovered to be associated with coloration in R.pulchrum for the first time. The FNS gene existed in the form of FNSI. The IFR gene and its related metabolites of medicarpin derivatives were highly expressed in purple petal. In cultivar 'Fenhe', up-regulation of F3'H and F3'5'H and down-regulation of 4CL, DFR, ANS, and GT were associated with pink coloration. With the transcription factor analysis, a subfamily of DREBs was found to be specifically enriched in pink petals. This suggested that the DREB family play an important role in pink coloration. In cultivars 'Baihe', flavonoid biosynthesis was inhibited by low expression of CHS, while pigment accumulation was inhibited by low expression of F3'5'H, DFR, and GT, which led to a white coloration.
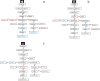
Conclusions: By analyzing the transcriptome and metabolome of R.pulchrum, principal differential expression genes and metabolites of flavonoid biosynthesis pathway were identified. Many novel metabolites, genes, and transcription factors associated with coloration have been discovered. To reveal the mechanism of the coloration of different petals, a model of the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway of R.pulchrum was constructed. These results provide in depth information regarding the coloration of the petals and the flavonoid metabolism of R.pulcherum. The study of transcriptome and metabolome profiling gains insight for further genetic improvement in Rhododendron.
Keywords: Flavonoid biosynthesis; Metabolome; Rhododendron pulchrum; Transcriptome.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
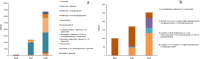
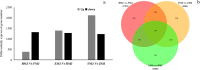


References
-
- Hang NTT, Miyajima I, Ureshino K, Masuda JI, Okubo H. Comparison of morphological characteristics of Rhododendron simsii. Planch distributed in Vietnam and Japan. J Faculty of Agriculture Kyushu Univ. 2010;55(2):233–237. doi: 10.5109/18835. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

