Magnitude and determinants of suicide among overweight reproductive-age women, Chacha and Debre Berhan Town, Ethiopia: community based cross-sectional study
- PMID: 35974397
- PMCID: PMC9382839
- DOI: 10.1186/s13033-022-00551-w
Magnitude and determinants of suicide among overweight reproductive-age women, Chacha and Debre Berhan Town, Ethiopia: community based cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: The magnitude and impact of women's suicidal behaviors, like suicidal ideation and suicidal attempts, are an important public health problem in low and middle-income countries, including Ethiopia. Suicidal behavior and being overweight are typical complications of reproductive age with many undesired consequences. Despite both having a serious impact on women of reproductive age, they are neglected in Ethiopia. Accordingly, this study aimed to examine the magnitude and determinants of suicide among overweight reproductive-age women in Chacha and Debre Berhan towns, Ethiopia.
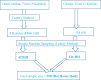
Methods: A community-based cross-sectional study design was once employed from April 1, 2020 to June 1, 2020. The Composite International Diagnostic Interview was used to measure suicidal attempts and ideation, and the data was collected by direct interview. All collected data were entered into Epi Data version 4.6 and analyzed with SPSS version 25. Bivariate and multivariable regression models were used to determine the factors associated with a suicidal attempt and ideation. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Result: Of the total participants, 523 were included, with a response rate of 93.7%. The prevalence of suicidal ideation was 13.0% (95% CI 10.1-15.9), whereas suicidal attempt was 2.3% (95% CI 1.1-3.6). Based on multivariable regression analysis, the odds of suicidal ideation have been higher among overweight women with stressful life events, depression, and younger age groups.
Conclusion: Suicidal ideation was frequent in overweight reproductive-age women. Preventing, treating, and using coping mechanisms regarding identified factors is a good way to minimize the burden of suicide.
Keywords: Overweight; Reproductive-age; Suicidal attempt; Suicidal ideation; Women.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors assure that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of Depression and Associated Factors Among Normal and Overweight Reproductive Age Women, Ethiopia: Community-Based Comparative Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Womens Health. 2021 Mar 22;13:337-347. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S301778. eCollection 2021. Int J Womens Health. 2021. PMID: 33790658 Free PMC article.
-
Magnitude and associated factors of suicidal ideation and attempt among people with epilepsy attending outpatient treatment at primary public hospitals in northwest Ethiopia: a multicentre cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2021 Jan 4;11(1):e043227. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-043227. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 33397668 Free PMC article.
-
Intimate partner violence and COVID-19 among reproductive age women: A community-based cross-sectional survey, Ethiopia.Womens Health (Lond). 2022 Jan-Dec;18:17455065211068980. doi: 10.1177/17455065211068980. Womens Health (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35098815 Free PMC article.
-
Suicidal behavior and associated factors among prisoners in Dilla town, Dilla, Ethiopia 2020: An institutional based cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2022 May 11;17(5):e0267721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267721. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35544553 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of suicidal ideation and attempted suicide in the general population of Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Ment Health Syst. 2021 Mar 24;15(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13033-021-00449-z. Int J Ment Health Syst. 2021. PMID: 33761982 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sadock BJ. Kaplan & Sadock's synopsis of psychiatry: behavioral sciences/clinical psychiatry. 11 ed. New York, 2015.
-
- Organization WH. Regional strategy on preventing suicide. 2018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous