Glenoid Morphology and Related Parameters in Turkish Society
- PMID: 35975093
- PMCID: PMC9375541
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.27959
Glenoid Morphology and Related Parameters in Turkish Society
Abstract
Introduction Glenoid morphology may vary in different ethnic groups. Detection of these differences may be important in preoperative planning, especially in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. In this study, we investigated the mean glenoid size and retroversion in Turkish society and their relationship with the dominant side, gender, height, weight, and body mass index (BMI). Materials and methods Between 2019 and 2021, 102 shoulders of 51 patients (24 females/27 males, 51 left/51 right) who were included in shoulder joint imaging during thorax CT scanning were examined. Those with glenoid fracture, arthrosis, shoulder surgery or deformity, or younger than 18 years of age were not included in the study. The mean age was 41.69 (range: 18-73) years. Glenoid anterior-posterior diameter (D) and glenoid version (GV) were measured in axial slices, and glenoid height (H) was measured in coronal slices. The correlation of these parameters with gender, height, weight, and dominant side was examined. Results Mean D was 25.79±4.44 mm, mean H was 29.08±4.08 mm, and mean GV was -0.99°±0.92°. The mean height of the patients was 162±16.23 cm and the mean weight was 71.9±15.36 kg. The glenoid diameter and height were smaller in females, however, no statistically significant difference was found in the glenoid version (p<0.01, p<0.01, and p=0.92). The glenoid on the dominant side was statistically significantly more retroverted, whereas D and H were not associated with dominance (p<0.01, p=0.9, and p=0.98). It was found that the glenoid sizes were very highly correlated with the patient's height, and it was highly correlated with the patient's weight (p<0.01 and p<0.01). On the other hand, height and weight were not correlated with the glenoid version (p=0.47 and p=0.81, respectively). There was no statistically significant relationship between BMI and glenoid sizes and glenoid version (p=0.14 and p=0.46, respectively). Conclusions Females in Turkish society had small glenoid sizes. Male gender, height, and weight were positively correlated with large glenoids. The glenoid was more retroverted on the dominant side. These findings should be considered in preoperative planning in Turkish society.
Keywords: computed tomography; ethnicity; gender; glenoid morphology; related parameters.
Copyright © 2022, Karademir et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
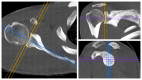

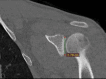

References
-
- Risks of loosening of a prosthetic glenoid implanted in retroversion. Farron A, Terrier A, Büchler P. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15:521–526. - PubMed
-
- Three-dimensional planning and use of patient-specific guides improve glenoid component position: an in vitro study. Walch G, Vezeridis PS, Boileau P, Deransart P, Chaoui J. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24:302–309. - PubMed
-
- Glenoid version and size: does gender, ethnicity, or body size play a role? Piponov HI, Savin D, Shah N, Esposito D, Schwartz B, Moretti V, Goldberg B. Int Orthop. 2016;40:2347–2353. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
