Flow Cytometric DNA Ploidy Analysis in Haemato-Lymphoid Neoplasms: An Analysis of 132 Cases
- PMID: 35975117
- PMCID: PMC9339125
- DOI: 10.18502/ijhoscr.v16i1.8440
Flow Cytometric DNA Ploidy Analysis in Haemato-Lymphoid Neoplasms: An Analysis of 132 Cases
Abstract
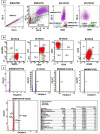
Background: FxCycleTM Violet (FCV) based flow cytometric (FCM) DNA ploidy analysis is a rapid and simple tool that can substantiate in characterizing the biological behaviour across the spectrum of haematological malignancies and correlates with cytogenetic studies. Materials and Methods: In this prospective study, we performed simultaneous immunophenotyping with FCV based on ploidy analysis in n=132 consecutive new samples, comprising n=110 samples of haemato-lymphoid neoplasms, including acute leukemias (n=67, 60.9%), CML with myeloid blast crisis (n=1, 0.9%), MDS with excess blasts (n=2, 1.8%), mature B cell/ T cell neoplasms (n=37, 33.7%), multiple myeloma (n=3, 2.7%) along with n=22 normal samples. The FCM DNA data was compared with corresponding conventional karyotyping results, wherever available. Results: In FCM ploidy analysis (n=110), the overall DNA index (DI) ranged from 0.81 to 2.17 and S-Phase fraction (SPF) from 0.1-31.6%. Diploidy was seen in n = 90 (81.8%), low-hyperdiploidy in n = 10 (9.1%), high-hyperdiploidy in n = 7 (6.4%) with one case each (0.9% each) having near-tetraploidy, high-hypodiploidy and low-hypodiploidy. The DI of all viable cell populations in normal samples ranged from 0.96-1.05. Conventional karyotyping was performed in n=76/110 cases (70%) with n= 11/76 (15%) culture failures. The modal chromosome number ranged from 45 to 63. A concordance of 95.4% (n=62/65) was noted with corresponding FCM DI. Conclusion: FCV-based ploidy is a sensitive technique that provides complementary information and ascertains a strong correlation with conventional cytogenetics across all haemato-lymphoid neoplasms. It can detect aneuploidy in all B-ALL and myeloma cases, even in hemodiluted samples with cytogenetic culture failure; supplement the diagnoses of erythroleukemia, and provide a useful screen for a higher grade lymph node disease in lymphoma cases with SPF > 3%.
Keywords: Cytogenetics; DNA ploidy; FxCycle™ violet; Karyotyping; S-phase fraction.
Copyright © 2022 Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FxCycle™ Based Ploidy Correlates with Cytogenetic Ploidy in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Is Able to Detect the Aneuploid Minimal Residual Disease Clone.Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2019 Sep;96(5):359-367. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.21765. Epub 2019 Feb 4. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2019. PMID: 30715800
-
A novel and easy FxCycle™ violet based flow cytometric method for simultaneous assessment of DNA ploidy and six-color immunophenotyping.Cytometry A. 2016 Mar;89(3):281-91. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.22803. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Cytometry A. 2016. PMID: 26671309
-
Detecting hypodiploidy with endoreduplication and masked hypodiploidy in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia using multicolor flow cytometry.Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2022 May;102(3):199-208. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.22063. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2022. PMID: 35212133
-
Prognostic significance of DNA ploidy in oral squamous cell carcinomas. A retrospective flow and image cytometric study with comparison of DNA ploidy in excisional biopsy specimens and resection specimens, primary, tumors, and lymph node metastases.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995 Jan;79(1):68-76. doi: 10.1016/s1079-2104(05)80077-0. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995. PMID: 7614165 Review.
-
Prognostic significance of morphological parameters and flow cytometric DNA analysis in carcinoma of the breast.Pathol Annu. 1990;25 Pt 1:171-210. Pathol Annu. 1990. PMID: 2153277 Review.
References
-
- Yuan CM. A bright and colorful future for DNA cell cycle analysis. Cytometry A. 2016;89(3):236–8. - PubMed
-
- Duque RE, Andreeff M, Braylan RC, et al. Consensus review of the clinical utility of DNA flow cytometry in neoplastic hematopathology. Cytometry. 1993;14(5):492–6. - PubMed
-
- Tembhare P, Badrinath Y, Ghogale S, et al. A novel and easy FxCycle™ violet based flow cytometric method for simultaneous assessment of DNA ploidy and six-color immunophenotyping. Cytometry A. 2016;89(3):281–91. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
