Survival of Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: An Experience in Developing Country
- PMID: 35975120
- PMCID: PMC9339122
- DOI: 10.18502/ijhoscr.v16i1.8443
Survival of Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: An Experience in Developing Country
Abstract
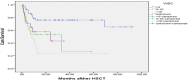
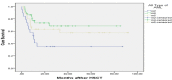
Background: Allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) is the highest potential treatment for long-term survival as post-remission therapy for acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The aim of this study was to estimate the overall survival (OS) of patients with AML after allo-SCT and to identify the factors affecting them as a prognostic factor for the survival of patients. Material and Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, data of patients with AML who underwent allo-SCT at Taleghani bone marrow transplantation and cell therapy center in Tehran, Iran, from May 2009 to September 2016 were used. A total of 101 patients were enrolled and death time was considered as a failure event for them. Kaplan-Meier method, log-Rank tests, and Cox proportional hazard model were used to evaluate OS and to identify the risk factors of patient's survival. The SPSS software version 21 was used for the analysis of data and P<0.05 was considered as a significant level. Results: Of 101 patients with AML, 49 (48.5%) were males. The median age at allo-SCT was 32.76 years and 42 patients (41.6%) died. The 5-year OS and disease-free survival (DFS) was 56% (95%CI: 51-61%) and 52% (95%CI: 57-47%), respectively. Multivariate analysis by Cox regression indicated that OS has a significant relationship with primary WBC count and relapse (P=0.001). Conclusion: Our results showed that allo-SCT has nearly the same outcome in developing countries and the WBC count and relapse are effective factors on the chance of survival in AML patients after allo-SCT.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia; Allogeneic stem cell transplantation; Prognostic factors; Survival analysis.
Copyright © 2022 Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High prognostic value of pre-allogeneic stem cell transplantation minimal residual disease detection by WT1 gene expression in AML transplanted in cytologic complete remission.Leuk Res. 2017 Dec;63:22-27. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2017.10.010. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Leuk Res. 2017. PMID: 29096332
-
Predictive value of pretransplantation molecular minimal residual disease assessment by WT1 gene expression in FLT3-positive acute myeloid leukemia.Exp Hematol. 2017 May;49:25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2017.01.005. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Exp Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28159598
-
Clinical outcome of myeloid sarcoma in adult patients and effect of allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Results from a multicenter survey.Leuk Res. 2017 Feb;53:74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2016.12.003. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Leuk Res. 2017. PMID: 28056398
-
A review on allogeneic stem cell transplantation for newly diagnosed pediatric acute myeloid leukemia.Blood. 2010 Sep 30;116(13):2205-14. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-01-261800. Epub 2010 Jun 10. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20538803 Review.
-
The prognostic value of cytogenetics is reinforced by the kind of induction/consolidation therapy in influencing the outcome of acute myeloid leukemia--analysis of 848 patients.Leukemia. 2001 Jun;15(6):903-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402142. Leukemia. 2001. PMID: 11417475 Review.
Cited by
-
FT538, iPSC-derived NK cells, enhance AML cell killing when combined with chemotherapy.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jan;29(1):e70169. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70169. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39797701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khwaja A, Bjorkholm M, Gale RE, et al. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Nat Rev Dis Primers . 2016;2:16010. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
