Neural Net Modeling of Checkpoint Inhibitor Related Myocarditis and Steroid Response
- PMID: 35975122
- PMCID: PMC9376002
- DOI: 10.2147/CPAA.S369008
Neural Net Modeling of Checkpoint Inhibitor Related Myocarditis and Steroid Response
Abstract
Background: Serious but rare side effects associated with immunotherapy pose a difficult problem for regulators and practitioners. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have come into widespread use in oncology in recent years and are associated with rare cardiotoxicity, including potentially fatal myocarditis. To date, no comprehensive model of myocarditis progression and outcomes integrating time-series based laboratory and clinical signals has been constructed. In this paper, we describe a time-series neural net (NN) model of ICI-related myocarditis derived using supervised machine learning.
Methods: We extracted and modeled data from electronic medical records of ICI-treated patients who had an elevation in their troponin. All data collection was performed using an electronic case report form, with approximately 300 variables collected on as many occasions as available, yielding 6000 data elements per patient over their clinical course. Key variables were scored 0-5 and sequential assessments were used to construct the model. The NN model was developed in MatLab and applied to analyze the time course and outcomes of treatments.
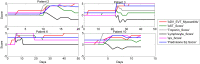
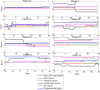
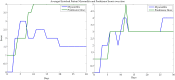
Results: We identified 23 patients who had troponin elevations related to their ICI therapy, 15 of whom had ICI-related myocarditis, while the remaining 8 patients on ICIs had other causes for troponin elevation, such as myocardial infarction. Our model showed that troponin was the most predictive biomarker of myocarditis, in line with prior studies. Our model also identified early and aggressive use of steroid treatment as a major determinant of survival for cases of grade 3 or 4 ICI-related myocarditis.
Conclusion: Our study shows that a supervised learning NN can be used to model rare events such as ICI-related myocarditis and thus provide clinical insight into drivers of progression and treatment outcomes. These findings direct attention to early detection biomarkers and clinical symptoms as the best means of implementing early and potentially life-saving steroid treatment.
Keywords: NN modeling; checkpoint inhibitor; dose and timing; myocarditis; steroid response.
© 2022 Stefanovic et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Andres Gomez-Caminero is an employee of Bristol Myers Squibb. Dr Igor Puzanov reports he has received consulting fees from Iovance, Nektar, Oncorus, Merck in past 2 years. Dr Jerome J Schentag reports grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, during the conduct of the study. The authors acknowledge Bristol Myers Squibb funded this work but have no other competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Myositis Overlapping With Myocarditis: An Institutional Case Series and a Systematic Review of Literature.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 12;13:884776. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.884776. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35645839 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics, time course, treatment and outcomes of patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jun;9(6):e002553. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002553. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34162715 Free PMC article.
-
Prognosis of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related myocarditis: Retrospective experience of a single institution.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Jul 30;136:112385. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112385. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38850788
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced myocarditis in cancer patients: a case report and review of reported cases.Cardiooncology. 2021 Aug 9;7(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s40959-021-00114-x. Cardiooncology. 2021. PMID: 34365980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Biomarkers in the Management of Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Myocarditis.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023 Sep;25(9):959-967. doi: 10.1007/s11886-023-01915-5. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37436648 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A review of immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and biomarkers.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025 Dec;21(1):2512645. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2512645. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40505635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence Applications in Cardio-Oncology: A Comprehensive Review.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2025 Feb 19;27(1):56. doi: 10.1007/s11886-025-02215-w. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39969610 Review.
-
Artificial intelligence and myocarditis-a systematic review of current applications.Heart Fail Rev. 2024 Nov;29(6):1217-1234. doi: 10.1007/s10741-024-10431-9. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Heart Fail Rev. 2024. PMID: 39138803 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a prediction tool for intraoperative blood transfusion in brain tumor resection surgery: a retrospective analysis.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 13;13(1):17428. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44549-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37833334 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

