Comparison between High-Power Short-Duration and Conventional Ablation Strategy in Atrial Fibrillation: An Updated Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35975140
- PMCID: PMC9355769
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1065077
Comparison between High-Power Short-Duration and Conventional Ablation Strategy in Atrial Fibrillation: An Updated Meta-Analysis
Abstract
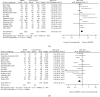
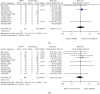
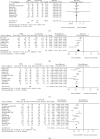
High-power short-duration (HPSD) setting during radiofrequency ablation has become an attempt to improve atrial fibrillation (AF) treatment outcomes. This study ought to compare the efficacy, safety, and effectiveness between HPSD and conventional settings. PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library were searched. Studies that compared HPSD and conventional radiofrequency ablation settings in AF patients were included while studies performed additional ablations on nonpulmonary vein targets without clear recording were excluded. Data were pooled with random-effect model. Efficacy endpoints include first-pass pulmonary vein isolation (PVI), acute pulmonary vein (PV) reconnection, free from AF, and free from atrial tachycardia (AT) during follow-up. Safety endpoints include esophagus injury rate and major complication rate. Effectiveness endpoints include complete PVI rate, total procedure time, PVI time, and PVI radiofrequency ablation (PVI RF) time. We included 22 studies with 3867 atrial fibrillation patients in total (2393 patients received HPSD radiofrequency ablation). Perioperatively, the HPSD group showed a higher first-pass PVI rate (risk ratio, RR = 1.10, P = 0.0001) and less acute PV reconnection rate (RR = 0.56, P = 0.0004) than the conventional group. During follow-up, free from AF (RR = 1.11, P = 0.16) or AT (RR = 1.06, P = 0.24) rate did not differ between HPSD and conventional groups 6-month postsurgery. However, the HPSD group showed both higher free from AF (RR = 1.17, P = 0.0003) and AT (RR = 1.11, P < 0.0001) rate than the conventional group 12-month postsurgery. The esophagus injury (RR = 0.99, P = 0.98) and major complications (RR = 0.76, P = 0.70) rates did not differ between the two groups. The HPSD group took shorter total procedure time (MD = -33.71 95% CI: -43.10 to -24.33, P < 0.00001), PVI time (MD = -21.60 95% CI: -25.00 to -18.21, P < 0.00001), and PVI RF time (MD = -13.72, 95% CI: -14.45 to -13.00, P < 0.00001) than conventional groups while complete procedure rate did not differ between two groups (RR = 1.00, P = 0.93). HPSD setting during AF radiofrequency ablation has better effectiveness, efficacy, and similar safety compared with the conventional setting.
Copyright © 2022 Mohan Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pulmonary vein isolation using pulsed field ablation vs. high-power short-duration radiofrequency ablation in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: efficacy, safety, and long-term follow-up (PRIORI study).Europace. 2024 Jul 2;26(7):euae194. doi: 10.1093/europace/euae194. Europace. 2024. PMID: 38996227 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of high-power short-duration and low-power long-duration radiofrequency ablation for treating atrial fibrillation: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Cardiol. 2020 Dec;43(12):1631-1640. doi: 10.1002/clc.23493. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Clin Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 33107625 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of high power short duration in atrial fibrillation ablation - a superior efficient ablation strategy.Acta Cardiol. 2022 Feb;77(1):14-32. doi: 10.1080/00015385.2021.1939512. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Acta Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 34218737 Review.
-
High-Power Short-Duration Posterior Wall Isolation in Addition to Pulmonary Vein Isolation in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Using the New TactiFlex™ Ablation Catheter.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Sep 20;11(9):294. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11090294. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 39330352 Free PMC article.
-
A Randomized Trial of High vs Standard Power Radiofrequency Ablation for Pulmonary Vein Isolation: SHORT-AF.JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2023 Jul;9(7 Pt 2):1038-1047. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2022.12.020. Epub 2023 Feb 22. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2023. PMID: 37495318 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Comparative Analysis of Clinical Outcomes of High-power, Short-duration Ablation versus Low-power, Long-duration Ablation Strategy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Comprehensive Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses.J Innov Card Rhythm Manag. 2024 Aug 15;15(8):5963-5980. doi: 10.19102/icrm.2024.15083. eCollection 2024 Aug. J Innov Card Rhythm Manag. 2024. PMID: 39193534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of the dispersive patch placement on dissipated power in radiofrequency ablation for pulmonary vein isolation via a virtual patient study.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 27;15(1):6986. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90158-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40011542 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

