Neighborhood, built environment and resilience in transportation during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 35975170
- PMCID: PMC9371985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trd.2022.103428
Neighborhood, built environment and resilience in transportation during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
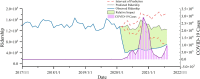
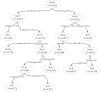
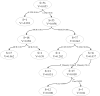
COVID-19 has swept the world, and the unprecedented decline in transit ridership has been noticed. However, little attention has been paid to the resilience of the transportation system, particularly in medium-sized cities. Drawing upon a light rail ridership dataset in Salt Lake County from 2017 to 2021, we develop a novel method to measure the vulnerability and resilience of transit ridership using a Bayesian structure time series model. The results show that government policies have a more significant impact than the number of COVID-19 cases on transit ridership. Regarding the built environment, a highly compact urban design might reduce the building coverage ratio and makes transit stations more vulnerable and less resilient. Furthermore, the high rate of minorities is the primary reason for the drops in transit ridership. The findings are valuable for understanding the vulnerability and resilience of transit ridership to pandemics for better coping strategies in the future.
Keywords: Bayesian structure time series; Build environment; COVID-19; Regression tree; Transit ridership.
© 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Transit environments for physical activity: Relationship between micro-scale built environment features surrounding light rail stations and ridership in Houston, Texas.J Transp Health. 2020 Dec;19:100924. doi: 10.1016/j.jth.2020.100924. Epub 2020 Aug 28. J Transp Health. 2020. PMID: 32904408 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of COVID-19 on urban rail transit ridership using the Synthetic Control Method.Transp Policy (Oxf). 2021 Sep;111:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.tranpol.2021.07.006. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Transp Policy (Oxf). 2021. PMID: 36568355 Free PMC article.
-
Disparities in the Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Public Transit Ridership in Austin, Texas, U.S.A.Transp Res Rec. 2023 Apr;2677(4):287-297. doi: 10.1177/03611981231159906. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Transp Res Rec. 2023. PMID: 37153206 Free PMC article.
-
Executive orders or public fear: What caused transit ridership to drop in Chicago during COVID-19?Transp Res D Transp Environ. 2022 Apr;105:103226. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2022.103226. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Transp Res D Transp Environ. 2022. PMID: 36570332 Free PMC article.
-
Towards building resilient cities to pandemics: A review of COVID-19 literature.Sustain Cities Soc. 2023 Feb;89:104326. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2022.104326. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Sustain Cities Soc. 2023. PMID: 36467253 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
COVID-19, Cities and Inequality.Appl Geogr. 2023 Nov;160:103059. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2023.103059. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Appl Geogr. 2023. PMID: 37841058 Free PMC article.
-
Metro travel and perceived COVID-19 infection risks: A case study of Hong Kong.Cities. 2023 Jun;137:104307. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2023.104307. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Cities. 2023. PMID: 37008809 Free PMC article.
-
Commercial dynamics in urban China during the COVID-19 recession: Vulnerability and short-term adaptation of commercial centers in Shanghai.Appl Geogr. 2023 Mar;152:102889. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2023.102889. Epub 2023 Jan 21. Appl Geogr. 2023. PMID: 36713474 Free PMC article.
-
On the bumpy road to recovery: resilience of public transport ridership during COVID-19 in 15 European cities.Lett Spat Resour Sci. 2023;16(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s12076-023-00338-8. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Lett Spat Resour Sci. 2023. PMID: 37035016 Free PMC article.
-
Green infrastructure inequality in the context of COVID-19: Taking parks and trails as examples.Urban For Urban Green. 2023 Aug;86:128027. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2023.128027. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Urban For Urban Green. 2023. PMID: 37614701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdullahi S., Pradhan B., Mansor S., Shariff A.R.M. GIS-based modeling for the spatial measurement and evaluation of mixed land use development for a compact city. GIScience Remote Sens. 2015;52(1):18–39.
-
- Albanesi S., Kim J. Effects of the COVID-19 recession on the U.S. labor market: occupation, family, and gender. J. Econ. Perspect. 2021;35(3):3–24.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
