Relationship Between Sporadic Renal Cysts and Renal Function Detected by Isotope Renography in Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 35975275
- PMCID: PMC9375979
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S373120
Relationship Between Sporadic Renal Cysts and Renal Function Detected by Isotope Renography in Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to reveal the relationship between the volume of sporadic renal cysts and renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Materials and methods: One hundred and seventy-one patients that underwent renal imaging and other routine examinations at the Shanghai Pudong Hospital were included in this study. The Gates' method of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) was measured by 99mTc-DTPA renal dynamic imaging in addition to the eGFR, calculated by the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation (CKD-EPI).
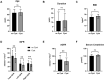
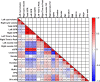
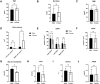
Results: Our results showed that BMI, total iGFR, and eGFR showed significant differences between patients with T2D with or without SRC (p < 0.05). Spearman correlation analysis showed that cyst volume was positively correlated with Scr and gender but not iGFR (p > 0.05). The total iGFR positively correlated with eGFR (r = 0.83, p < 0.0001) and negatively with Scr (r = -0.78, p < 0.0001), age (r = -0.43, p < 0.0001), duration of T2D (r = -0.25, p = 0.001), and BMI (r = -0.21, p = 0.006) but not gender (r = -0.03, p = 0.668). The multilinear regression model revealed that gender (β = 0.346, p < 0.001), iGFR (β = -0.705, p < 0.001), and serum uric acid (β = 0.195, p = 0.032) were independent predictors of Scr. Moreover, we observed a significant increase in Scr in males (p < 0.05). Finally, we found that the split kidney function reflected by iGFR and related parameters such as time to peak (PTT) and half time of excretion (excrete t1/2) did not mutually distinguish from each other significantly whether they are measured in patients with renal cysts or in those without renal cysts (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: Our preliminary results suggest that in T2D, SRCs may be a renal complication of diabetic nephropathy. Although we found that the patients with renal cysts may display reduced iGFR, the volume of simple cysts seems not to exacerbate renal insufficiency. Isotope renography is a useful tool to evaluate the split kidney functions in diabetic patients who acquire single-side cysts.
Keywords: SRCs; cysts volume; gender disparity; isotope glomerular filtration rate; kidney function; type 2 diabetes.
© 2022 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
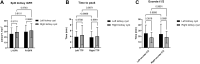
Similar articles
-
Glomerular filtration rate measured by (99m) Tc-DTPA renal dynamic imaging is significantly lower than that estimated by the CKD-EPI equation in horseshoe kidney patients.Nephrology (Carlton). 2016 Jun;21(6):499-505. doi: 10.1111/nep.12663. Nephrology (Carlton). 2016. PMID: 26517584 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical application of full age spectrum formula based on serum creatinine in patients with chronic kidney disease].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Sep;30(9):877-881. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.09.011. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 30309415 Chinese.
-
Feasibility of gamma camera-based GFR measurement using renal depth evaluated by lateral scan of 99mTc-DTPA renography.Ann Nucl Med. 2020 May;34(5):349-357. doi: 10.1007/s12149-020-01455-w. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Ann Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 32166712
-
Determination of the glomerular filtration rate in patients with type 2 diabetes: An assessment of the agreement between 51Cr-EDTA plasma clearance and 99mTc-DTPA plasma clearance, 99mTc-DTPA renography and plasma creatinine prediction equation.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020 Mar;161:108079. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108079. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 32057963
-
Comparison of Performance of Improved Serum Estimators of Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) to 99mTc-DTPA GFR Methods in Patients with Hepatic Cirrhosis.J Nucl Med Technol. 2017 Mar;45(1):42-49. doi: 10.2967/jnmt.116.180851. Epub 2017 Feb 2. J Nucl Med Technol. 2017. PMID: 28154020 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Decline in measured glomerular filtration rate is associated with simple renal cyst in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes.J Diabetes Investig. 2024 Jan;15(1):26-33. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14120. Epub 2023 Dec 11. J Diabetes Investig. 2024. PMID: 38078509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xie P, Huang JM, Liu XM, Wu WJ, Pan LP, Lin HY. (99m)Tc-DTPA renal dynamic imaging method may be unsuitable to be used as the reference method in investigating the validity of CDK-EPI equation for determining glomerular filtration rate. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e62328. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062328 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pal DK, Kundu AK, Das S. Simple renal cyst: an observation. J Indian Med Assoc. 1997;95(10):555, 558. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

