Expression of Calbindin-D28K in the Developing and Adult Mouse Cochlea
- PMID: 35975307
- PMCID: PMC9393511
- DOI: 10.1369/00221554221119543
Expression of Calbindin-D28K in the Developing and Adult Mouse Cochlea
Abstract
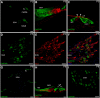
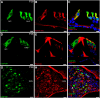
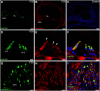
Herein, we aimed to use double-labeling immunofluorescence to describe the expression pattern of Calbindin-D28K (CaBP28K) in the mouse cochlea from late embryonic (E) stages to the adulthood. CaBP28K was expressed in the inner hair cells (IHCs) and the greater epithelial ridge (GER) at E17. In addition, its expression was observed in the interdental cells. On postnatal day 1 (P1), CaBP28K immunoreactivity was observed in the IHCs and outer hair cells (OHCs) and was also specifically expressed in the nucleus and the cytoplasm of spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs). At P8, CaBP28K labeling disappeared from the interdental cells, and the CaBP28K-positive domain within the GER shifted from the entire cytoplasm to only the apical and basal regions. At P14, CaBP28K immunoreactivity was lost from the GER; however, its expression in the IHCs and OHCs, as well as the SGNs, persisted into adulthood. The identification of CaBP28K in the hair cells (HCs) and cuticular plates, as well as SGNs, was confirmed by its colocalization with several markers for Sox2, Myosin VIIa, Phalloidin, and Tuj1. We also detected colocalization with calmodulin in the cytoplasm of both HCs and SGNs. Western blot revealed an increase in CaBP28K postnatal expression in the mouse cochlea.
Keywords: Ca2+-binding proteins; cochlear development; immunohistochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Developmental expression of calretinin in the mouse cochlea.Eur J Histochem. 2024 Nov 6;68(4):4137. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2024.4137. Eur J Histochem. 2024. PMID: 39508782 Free PMC article.
-
Preferentially regulated expression of connexin 43 in the developing spiral ganglion neurons and afferent terminals in post-natal rat cochlea.Eur J Histochem. 2015 Feb 11;59(1):2464. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2015.2464. Eur J Histochem. 2015. PMID: 25820563 Free PMC article.
-
Appearance and distribution of two Ca2+-binding proteins during development of the cochlea in the musk shrew.Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1998 Sep 10;110(1):7-19. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(98)00087-x. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1998. PMID: 9733905
-
Development of calretinin immunoreactivity in the mouse inner ear.J Comp Neurol. 1994 Aug 22;346(4):517-29. doi: 10.1002/cne.903460405. J Comp Neurol. 1994. PMID: 7983242
-
Recent advances in the development and function of type II spiral ganglion neurons in the mammalian inner ear.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 May;65:80-87. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.09.017. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 27760385 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental expression of high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in the mouse cochlea.Eur J Histochem. 2023 Sep 1;67(3):3704. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2023.3704. Eur J Histochem. 2023. PMID: 37667832 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental expression of calretinin in the mouse cochlea.Eur J Histochem. 2024 Nov 6;68(4):4137. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2024.4137. Eur J Histochem. 2024. PMID: 39508782 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of S100β during mouse cochlear development.Eur J Histochem. 2025 Jan 21;69(1):4189. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2025.4189. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Eur J Histochem. 2025. PMID: 40066753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berggard T, Miron S, Onnerfjord P, Thulin E, Akerfeldt KS, Enghild JJ, Akke M, Linse S. Calbindin D28k exhibits properties characteristic of a Ca2+ sensor. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(19):16662–72. - PubMed
-
- Dechesne CJ, Lavigne-Rebillard M, Brehier A, Thomasset M, Sans A. Appearance and distribution of neuron-specific enolase and calbindin (CaBP 28 kDa) in the developing human inner ear. Brain Res. 1988;469(1–2):221–30. - PubMed
-
- Fischer N, Johnson CL, Majerus A, Potrusil T, Riechelmann H, Schmutzhard J, Schrott-Fischer A, Glueckert R. Age-dependent calcium-binding protein expression in the spiral ganglion and hearing performance of C57BL/6J and 129/SvJ mice. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2019;81(2–3):138–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

