Supplementing Glycine and N-Acetylcysteine (GlyNAC) in Older Adults Improves Glutathione Deficiency, Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Inflammation, Physical Function, and Aging Hallmarks: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 35975308
- PMCID: PMC9879756
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glac135
Supplementing Glycine and N-Acetylcysteine (GlyNAC) in Older Adults Improves Glutathione Deficiency, Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Inflammation, Physical Function, and Aging Hallmarks: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
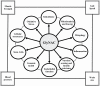
Background: Elevated oxidative stress (OxS), mitochondrial dysfunction, and hallmarks of aging are identified as key contributors to aging, but improving/reversing these defects in older adults (OA) is challenging. In prior studies, we identified that deficiency of the intracellular antioxidant glutathione (GSH) could play a role and reported that supplementing GlyNAC (combination of glycine and N-acetylcysteine [NAC]) in aged mice improved GSH deficiency, OxS, mitochondrial fatty-acid oxidation (MFO), and insulin resistance (IR). To test whether GlyNAC supplementation in OA could improve GSH deficiency, OxS, mitochondrial dysfunction, IR, physical function, and aging hallmarks, we conducted a placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial.
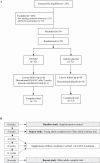
Methods: Twenty-four OA and 12 young adults (YA) were studied. OA was randomized to receive either GlyNAC (N = 12) or isonitrogenous alanine placebo (N = 12) for 16-weeks; YA (N = 12) received GlyNAC for 2-weeks. Participants were studied before, after 2-weeks, and after 16-weeks of supplementation to assess GSH concentrations, OxS, MFO, molecular regulators of energy metabolism, inflammation, endothelial function, IR, aging hallmarks, gait speed, muscle strength, 6-minute walk test, body composition, and blood pressure.
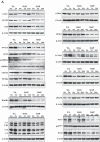
Results: Compared to YA, OA had GSH deficiency, OxS, mitochondrial dysfunction (with defective molecular regulation), inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, IR, multiple aging hallmarks, impaired physical function, increased waist circumference, and systolic blood pressure. GlyNAC (and not placebo) supplementation in OA improved/corrected these defects.
Conclusion: GlyNAC supplementation in OA for 16-weeks was safe and well-tolerated. By combining the benefits of glycine, NAC and GSH, GlyNAC is an effective nutritional supplement that improves and reverses multiple age-associated abnormalities to promote health in aging humans. Clinical Trials Registration Number: NCT01870193.
Keywords: Clinical trials; GlyNAC; Metabolism; Oxidative stress; Successful aging.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Gerontological Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Comment in
-
Toward Healthy Aging: A Clinical Trial Builds on Mechanistic Insights.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023 Jan 26;78(1):73-74. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glac200. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36702765 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health. Accessed Jan 2022.
-
- Cosentino F, Osto E. Aging and endothelial dysfunction. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2007;37(1–2):143–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

