Proteasome granule formation is regulated through mitochondrial respiration and kinase signaling
- PMID: 35975718
- PMCID: PMC9482347
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.259778
Proteasome granule formation is regulated through mitochondrial respiration and kinase signaling
Abstract
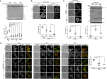
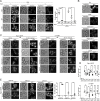
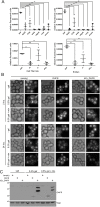
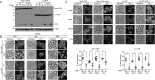
In the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, proteasomes are enriched in cell nuclei, in which they execute important cellular functions. Nutrient stress can change this localization, indicating that proteasomes respond to the metabolic state of the cell. However, the signals that connect these processes remain poorly understood. Carbon starvation triggers a reversible translocation of proteasomes to cytosolic condensates known as proteasome storage granules. Surprisingly, we observed strongly reduced levels of proteasome granules when cells had active cellular respiration prior to starvation. This suggests that the mitochondrial activity of cells is a determining factor in the response of proteasomes to carbon starvation. Consistent with this, upon inhibition of mitochondrial function, we observed that proteasomes relocalize to granules. These links between proteasomes and metabolism involve specific signaling pathways, as we identified a mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade that is critical to the formation of proteasome granules after respiratory growth but not following glycolytic growth. Furthermore, the yeast homolog of AMP kinase, Snf1, is important for proteasome granule formation induced by mitochondrial inhibitors, but it is dispensable for granule formation following carbon starvation. We propose a model in which mitochondrial activity promotes nuclear localization of the proteasome. This article has an associated First Person interview with the first author of the paper.
Keywords: AMP kinase; Autophagy; MAP kinases; Mitochondrial inhibition; Mitochondrial respiration; Proteaphagy; Proteasome; Proteasome storage granules.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Proteasome storage granules protect proteasomes from autophagic degradation upon carbon starvation.Elife. 2018 Apr 6;7:e34532. doi: 10.7554/eLife.34532. Elife. 2018. Retraction in: Elife. 2022 Sep 02;11:e82988. doi: 10.7554/eLife.82988. PMID: 29624167 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
To save or degrade: balancing proteasome homeostasis to maximize cell survival.Autophagy. 2018;14(11):2029-2031. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1515531. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Autophagy. 2018. PMID: 30204036 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasomes, Sir2, and Hxk2 form an interconnected aging network that impinges on the AMPK/Snf1-regulated transcriptional repressor Mig1.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jan 28;11(1):e1004968. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004968. eCollection 2015 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25629410 Free PMC article.
-
Microautophagy regulates proteasome homeostasis.Curr Genet. 2020 Aug;66(4):683-687. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01059-x. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 32077993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular localization of the proteasome in response to stress conditions.J Biol Chem. 2022 Jul;298(7):102083. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102083. Epub 2022 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35636514 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Yeast Protein Kinase Sch9 Functions as a Central Nutrient-Responsive Hub That Calibrates Metabolic and Stress-Related Responses.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jul 26;9(8):787. doi: 10.3390/jof9080787. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37623558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteasome condensate formation is driven by multivalent interactions with shuttle factors and ubiquitin chains.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Mar 5;121(10):e2310756121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2310756121. Epub 2024 Feb 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38408252 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasome dynamics in response to metabolic changes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Mar 3;13:1523382. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1523382. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40099196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A dynamic actin cytoskeleton is required to prevent constitutive VDAC-dependent MAPK signalling and aberrant lipid homeostasis.iScience. 2023 Aug 2;26(9):107539. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107539. eCollection 2023 Sep 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37636069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boos, F., KräMer, L., Groh, C., Jung, F., Haberkant, P., Stein, F., Wollweber, F., Gackstatter, A., Zöller, E., Van Der Laan, M.et al. . (2019). Mitochondrial protein-induced stress triggers a global adaptive transcriptional programme. Nat. Cell Biol. 21:442-451. 10.1038/s41556-019-0294-5 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

