Sildenafil Inhibits the Growth and Epithelial-to-mesenchymal Transition of Cervical Cancer via the TGF-β1/Smad2/3 Pathway
- PMID: 35975844
- PMCID: PMC10173468
- DOI: 10.2174/1568009622666220816114543
Sildenafil Inhibits the Growth and Epithelial-to-mesenchymal Transition of Cervical Cancer via the TGF-β1/Smad2/3 Pathway
Abstract
Aims: The study aims to explore new potential treatments for cervical cancer.
Background: Cervical cancer is the second most common cancer in women, causing >250,000 deaths worldwide. Patients with cervical cancer are mainly treated with platinum compounds, which often cause severe toxic reactions. Furthermore, the long-term use of platinum compounds can reduce the sensitivity of cancer cells to chemotherapy and increase the drug resistance of cervical cancer. Therefore, exploring new treatment options is meaningful for cervical cancer.
Objective: The present study was to investigate the effect of sildenafil on the growth and epithelial-tomesenchymal transition (EMT) of cervical cancer.
Methods: HeLa and SiHa cells were treated with sildenafil for different durations. Cell viability, clonogenicity, wound healing, and Transwell assays were performed. The levels of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), transforming growth factor-β type I receptor (TβRI), phosphorylated (p-) Smad2 and p-Smad3 in cervical cancer samples were measured. TGF-β1, Smad2 or Smad3 were overexpressed in HeLa cells, and we measured the expression of EMT marker proteins and the changes in cell viability, colony formation, etc. Finally, HeLa cells were used to establish a nude mouse xenograft model with sildenafil treatment. The survival rate of mice and the tumor size were recorded.
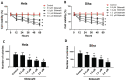
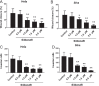
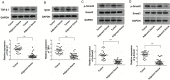
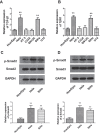
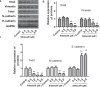
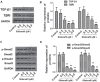
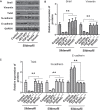
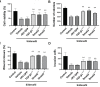
Results: High concentrations of sildenafil (1.0-2.0 μM) reduced cell viability, the number of HeLa and SiHa colonies, and the invasion/migration ability of HeLa and SiHa cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The expression of TGF-β1, TβRI, p-Smad2 and p-Smad3 was significantly enhanced in cervical cancer samples and cervical cancer cell lines. Sildenafil inhibited the expression of TGF-β1-induced EMT marker proteins (Snail, vimentin, Twist, E-cadherin and N-cadherin) and p-Smad2/3 in HeLa cells. Overexpression of TGF-β1, Smad2, and Smad3 reversed the effect of sildenafil on EMT, viability, colony formation, migration, and invasion ability of HeLa cells. In the in vivo study, sildenafil significantly increased mouse survival rates and suppressed xenograft growth.
Conclusion: Sildenafil inhibits the proliferation, invasion ability, and EMT of human cervical cancer cells by regulating the TGF-β1/Smad2/3 pathway.
Keywords: Sildenafil; cervical cancer; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; invasion; migration; platinum.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β1 (TGF-β1)-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via Decreased Pyruvate Kinase M2 (PKM2) Expression in Cervical Cancer Cells.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Apr 27;23:2017-2028. doi: 10.12659/msm.901542. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28446743 Free PMC article.
-
Glaucocalyxin A reverses EMT and TGF-β1-induced EMT by inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad2/3 signaling pathway in osteosarcoma.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Jul 1;307:158-166. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.05.005. Epub 2019 May 4. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 31059706
-
Suppressing effects of green tea extract and Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) on TGF-β- induced Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via ROS/Smad signaling in human cervical cancer cells.Gene. 2021 Aug 20;794:145774. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2021.145774. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Gene. 2021. PMID: 34126197
-
Nagilactone E suppresses TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer cells.Phytomedicine. 2019 Jan;52:32-39. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.222. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30599910
-
Babao Dan inhibits the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the TGF-β/Smad pathway.J Int Med Res. 2020 Jun;48(6):300060520925598. doi: 10.1177/0300060520925598. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32529872 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Drug Repurposing: Focus on Vasodilators.Cells. 2023 Feb 20;12(4):671. doi: 10.3390/cells12040671. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36831338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and Antitumor Activity of Brominated-Ormeloxifene (Br-ORM) against Cervical Cancer.ACS Omega. 2023 Oct 12;8(42):38839-38848. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02277. eCollection 2023 Oct 24. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37901538 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β-mediated activation of fibroblasts in cervical cancer: implications for tumor microenvironment and prognosis.PeerJ. 2025 Mar 19;13:e19072. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19072. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40124621 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor sildenafil as a therapeutic agent to prevent gastric cancer growth through suppressing c-MYC stability for IL-6 transcription.Commun Biol. 2025 Jan 18;8(1):85. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07519-9. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 39827331 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

