Suprascapular nerve blockage for painful shoulder pathology - a systematic review and meta-analysis of treatment techniques
- PMID: 35976156
- PMCID: PMC10471442
- DOI: 10.1308/rcsann.2022.0026
Suprascapular nerve blockage for painful shoulder pathology - a systematic review and meta-analysis of treatment techniques
Abstract
Background: Suprascapular nerve blockade (SSNB) through injection (SSNBi) and/or pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) provide options for the management of painful shoulder pathology. Multiple techniques for delivery of SSNB are described but no consensus on optimal symptom control is available. This systematic review and meta-analysis aims to assess patient-focussed outcomes in SSNB and explore the impact of variation in the technical application of this treatment modality.
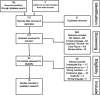
Methods: MEDLINE, Embase and CINAHL were searched for case series, cohort studies and randomised control trials published from database inception until 28 January 2021. Articles reporting use of SSNBi or PRF for treatment of shoulder pain with a minimum 3 months follow-up were included. Patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) were extracted and the pooled standardised mean difference (SMD), weighted by study size, was reported. Quality of methodology was assessed using Wylde's nonsummative four-point system.
Findings: Of 758 references, 18 studies were included, totalling 704 SSNB. Average pain improvement at 3 months was 52.3%, with meta-analysis demonstrating a SMD of 2.37. Whereas SSNBi combined with PRF shows the greatest SMD of 2.75, this did not differ significantly from SSNBi or PRF when used as monotherapy. Location of treatment and the guidance technique used did not influence outcome.
Conclusion: SSNBi and PRF provide safe and effective treatment for shoulder pain, as judged by PROMs. This may be of particular value in aging or comorbid patients and with surgical restrictions during the COVID-19 pandemic. Regardless of technique, patients experience a marked improvement in pain that is maintained beyond 3 months.
Keywords: Nerve block; Pain; Suprascapular nerve.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest. All authors had full access to all the data in the study, and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Figures
References
-
- Linsell L, Dawson J, Zondervan Ket al. . Prevalance and incidence of adults consulting for shoulder conditions in UK primary care; patterns of diagnosis and referral. Rhematology (Oxford) 2006; 45: 215–221. - PubMed
-
- Östör A, Richards C, Prevost Aet al. . Diagnosis and relation to general health of shoulder disorders presenting to primary care. Rheumatology 2005; 44: 800–805. - PubMed
-
- Wood RM. Modelling the impact of COVID-19 on elective waiting times. J Simul 2022; 16: 101–109.
-
- Abdelshaf ME, Yosry M, Elmulla AFet al. . Relief of chronic shoulder pain: a comparative study of three approaches. Middle East J Anesthesiol 2011; 21: 83–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical