Ranolazine Versus Allopurinol for Eligible Symptomatic Patients With a History of Angioplasty: Comparative Efficacy Study
- PMID: 35976197
- PMCID: PMC9434395
- DOI: 10.2196/39778
Ranolazine Versus Allopurinol for Eligible Symptomatic Patients With a History of Angioplasty: Comparative Efficacy Study
Abstract
Background: Recurrent angina, which is defined as a return of chest pain or chest discomfort, occurs in many patients undergoing coronary interventions.
Objective: This study aims to compare the antianginal efficacy of ranolazine versus allopurinol for eligible symptomatic patients with a history of angioplasty.
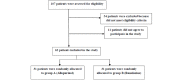
Methods: A total of 62 eligible symptomatic patients with a history of angioplasty were randomly allocated into two groups. For group A, 300 mg of allopurinol was administered twice daily, while for group B, 1000 mg of ranolazine daily was prescribed for a duration of 4 weeks. An initial screening visit was done for all participants where patients' medical history was recorded and a physical examination was given; electrocardiography, blood pressure, and heart rate measurements were done as well. The patients were also given a blood and exercise test. At the end of the medication period, participants were revisited, and the tests were done again. All the required data were collected via a researcher-made form, and data analysis was conducted using SPSS. The study was approved by a formal ethics committee.
Results: The mean age of participants in the two groups (A and B) was 57.36 (SD 8.36) and 60.27 (SD 9.17) years, respectively. Among the 62 patients, 34 (59%) were men, while 28 (41%) were women. Creatinine, fasting blood sugar, C-reactive protein, N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic protein, uric acid, white blood cell, and hemoglobin levels of participants were not significantly different between groups (P>.05). Both allopurinol and ranolazine increased the total exercise time and decreased the ST depression of the patients. Additionally, they both improved the chest pain severity and Duke Treadmill Score of patients. At the same time, ranolazine had a statistically greater effect on ST depression reduction (mean 2.64, SD 0.74 vs mean 1.57, SD 0.49), while allopurinol showed better efficacy in reducing chest pain severity (mean 1.86, SD 0.37 vs mean 0.59, SD 0.21) and the Duke Treadmill Score (mean -14.77, SD 3.65 vs mean -6.88, SD 1.93).
Conclusions: Based on the results, the antianginal efficacy of allopurinol and ranolazine was approved but with different effects on ST depression, chest pain severity, and the Duke Treadmill Score. Therefore, the precise differences in their effects need to be explored further.
Keywords: allopurinol; exercise tolerance; ranolazine; recurrent angina.
©Reza Rahmani, Ehsan Moradi Farsani, Sima Bahrami. Originally published in the Interactive Journal of Medical Research (https://www.i-jmr.org/), 17.08.2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Similar articles
-
Effects of ranolazine with atenolol, amlodipine, or diltiazem on exercise tolerance and angina frequency in patients with severe chronic angina: a randomized controlled trial.JAMA. 2004 Jan 21;291(3):309-16. doi: 10.1001/jama.291.3.309. JAMA. 2004. PMID: 14734593 Clinical Trial.
-
Double-blind efficacy and safety study of a novel anti-ischemic agent, ranolazine, versus placebo in patients with chronic stable angina pectoris. Ranolazine Study Group.Circulation. 1994 Aug;90(2):726-34. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.2.726. Circulation. 1994. PMID: 8044941 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term safety of a novel antianginal agent in patients with severe chronic stable angina: the Ranolazine Open Label Experience (ROLE).J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007 Mar 13;49(10):1027-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.10.067. Epub 2007 Feb 26. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17349881 Clinical Trial.
-
Ranolazine: effects on ischemic heart.Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2013 Dec;8(3):197-203. doi: 10.2174/15748901113089990023. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23961914 Review.
-
Ranolazine: a review of its use in chronic stable angina pectoris.Drugs. 2006;66(5):693-710. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200666050-00010. Drugs. 2006. PMID: 16620147 Review.
Cited by
-
Allopurinol versus Trimetazidine as Antianginal: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024 Aug;121(8):e20240500. doi: 10.36660/abc.20240500. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39292120 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. No abstract available.
-
2023 Guidelines of the Taiwan Society of Cardiology on the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Coronary Syndrome.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2023 Jan;39(1):4-96. doi: 10.6515/ACS.202301_39(1).20221103A. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2023. PMID: 36685161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shahsavari S, Nazari F, Karimyar JM, Sadeghi M. Epidemiologic study of hospitalized cardiovascular patients in Jahrom hospitals in 2012-2013. Cardiovasc Nurs J. 2013:14–21. http://journal.icns.org.ir/article-1-173-en.html
-
- Yousefnejhad K, Masoumi S. Evaluation of long-term clinical outcome of metal stent angioplasty in patients with coronary artery disease in Sari Fetemeh Zahra hospital from 2004 to 2006. Med J Mazandaran University Med Sci. 2007;17(62):21–30. https://jmums.mazums.ac.ir/article-1-453-fa.pdf
-
- Izzo P, Macchi A, De Gennaro L, Gaglione A, Di Biase M, Brunetti ND. Recurrent angina after coronary angioplasty: mechanisms, diagnostic and therapeutic options. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2012 Jul;1(2):158–69. doi: 10.1177/2048872612449111. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/24062904 10.1177_2048872612449111 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rajendra NS, Ireland S, George J, Belch JJF, Lang CC, Struthers AD. Mechanistic insights into the therapeutic use of high-dose allopurinol in angina pectoris. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Aug 16;58(8):820–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.12.052. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0735-1097(11)01948-6 S0735-1097(11)01948-6 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chaitman BR, Skettino SL, Parker JO, Hanley P, Meluzin J, Kuch J, Pepine CJ, Wang W, Nelson JJ, Hebert DA, Wolff AA, MARISA Investigators Anti-ischemic effects and long-term survival during ranolazine monotherapy in patients with chronic severe angina. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004 May 21;43(8):1375–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2003.11.045. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0735109704001925 S0735109704001925 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials