Analysis of INSPPIRE-2 Cohort: Risk Factors and Disease Burden in Children With Acute Recurrent or Chronic Pancreatitis
- PMID: 35976273
- PMCID: PMC9617760
- DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000003590
Analysis of INSPPIRE-2 Cohort: Risk Factors and Disease Burden in Children With Acute Recurrent or Chronic Pancreatitis
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this study is to investigate risk factors and disease burden in pediatric acute recurrent pancreatitis (ARP) and chronic pancreatitis (CP).
Methods: Data were obtained from INternational Study group of Pediatric Pancreatitis: In search for a cuRE-2 (INSPPIRE-2), the largest multi-center prospective cohort study in pediatric patients with ARP or CP.
Results: Of 689 children, 365 had ARP (53%), 324 had CP (47%). CP was more commonly associated with female sex, younger age at first acute pancreatitis (AP) attack, Asian race, family history of CP, lower BMI%, genetic and obstructive factors, PRSS1 mutations and pancreas divisum. CFTR mutations, toxic-metabolic factors, medication use, hypertriglyceridemia, Crohn disease were more common in children with ARP. Constant or frequent abdominal pain, emergency room (ER) visits, hospitalizations, medical, endoscopic or surgical therapies were significantly more common in CP, episodic pain in ARP. A total of 33.1% of children with CP had exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI), 8.7% had diabetes mellitus. Compared to boys, girls were more likely to report pain impacting socialization and school, medical therapies, cholecystectomy, but no increased opioid use. There was no difference in race, ethnicity, age at first AP episode, age at CP diagnosis, duration of disease, risk factors, prevalence of EPI or diabetes between boys and girls. Multivariate analysis revealed that family history of CP, constant pain, obstructive risk factors were predictors of CP.
Conclusions: Children with family history of CP, constant pain, or obstructive risk factors should raise suspicion for CP.
Copyright © 2022 by European Society for European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
M.E.L. is on the Board of Directors of the National Pancreas Association and receives royalties from Millipore Inc and UpToDate. T.G. received a research grant from Vertex Pharmaceuticals, and she is a consultant for Cystic Fibrosis Foundation (CFF). A.U. is a member of American Board of Pediatrics, Subboard of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Associate Editor of Pancreatology, and consultant for CFF. S.J.S. is a consultant for UpToDate, Nestle, Abbvie, and the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, and she has a grant from Gilead. V.D.M. is an Associate Editor for JPGN Reports. The remaining authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
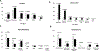
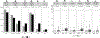
References
-
- Morinville VD, Barmada MM, Lowe ME Increasing incidence of acute pancreatitis at an American pediatric tertiary care center: is greater awareness among physicians responsible? Pancreas 2010;39(1):5–8. - PubMed
-
- Poddar U, Yachha SK, Borkar V, et al. A Report of 320 Cases of Childhood Pancreatitis: Increasing Incidence, Etiologic Categorization, Dynamics, Severity Assessment, and Outcome. Pancreas 2017;46(1):110–115. - PubMed
-
- Pant C, Sferra TJ Emergency Department Visits and Hospitalizations in Children With Chronic Pancreatitis in the United States. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2015;61(5):568–570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

