From clinical phenotype to proteinopathy: molecular neuroimaging in neurodegenerative dementias
- PMID: 35976328
- PMCID: PMC9491407
- DOI: 10.1590/0004-282X-ANP-2022-S138
From clinical phenotype to proteinopathy: molecular neuroimaging in neurodegenerative dementias
Abstract
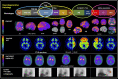
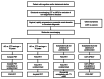
Neurodegenerative dementias are characterized by the abnormal accumulation of misfolded proteins. However, its diagnostic criteria are still based on the clinical phenotype. The development of biomarkers allowed in vivo detection of pathophysiological processes. This article aims to make a non-systematic review of the use of molecular neuroimaging as a biomarker. Molecular neuroimaging is based on the use of radiotracers for image acquisition. The radiotracer most used in PET is 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), with which it is possible to study the regional brain glucose metabolism. The pattern of regional hypometabolism provides neuroanatomical information on the neurodegenerative process, which, in turn, has a good specificity for each type of proteinopathy. FDG is very useful in the differential diagnosis of neurodegenerative dementias through the regional pattern of involvement, including dementia with Lewy bodies and the spectrum of frontotemporal dementia. More recently, radiotracers with specific ligands to some of the pathological proteins have been developed. Pittsburgh compound B (PIB) labeled with 11C and the ligands that use 18F (florbetapir, florbetaben and flutemetamol) are the most used radiotracers for the detection of insoluble β-amyloid peptide in Alzheimer's disease (AD). A first generation of ligands for tau protein has been developed, but it has some affinity for other non-tau protein aggregates. A second generation has the advantage of having a higher affinity for hyperphosphorylated tau protein, including in primary tauopathies.
As demências neurodegenerativas caracterizam-se pelo acúmulo anormal de proteínas mal dobradas. Entretanto, os seus critérios diagnósticos ainda se baseiam no fenótipo clínico. O desenvolvimento de biomarcadores permitiu a detecção in vivo do processo fisiopatológico. O objetivo deste artigo é fazer uma revisão não-sistemática sobre o papel da neuroimagem molecular como biomarcador. A neuroimagem molecular baseia-se no uso de radiotraçadores para aquisição da imagem. O mais usado no PET é o 18F-fluorodeoxiglicose (FDG), com o qual é possível estudar o metabolismo regional de glicose cerebral. O padrão de hipometabolismo regional fornece uma informação neuroanatômica do processo neurodegenerativo que, por sua vez, tem uma boa especificidade para cada tipo de proteinopatia. O PET-FDG é muito útil no diagnóstico diferencial das demências neurodegenerativas através do padrão de acometimento regional, incluindo a demência com corpos de Lewy e o espectro das demências frontotemporais. Mais recentemente, radiotraçadores com ligantes específicos a algumas das proteínas patológicas têm sido desenvolvidos. O composto B de Pittsburgh (PIB) com 11C e os ligantes dos que usam 18F (florbetapir, florbetaben e flutemetamol) são os radiotraçadores mais usados para a detecção de peptídeo β-amiloide insolúvel na doença de Alzheimer (DA). Uma primeira geração de ligantes para proteína tau foi desenvolvida, mas apresenta alguma afinidade a outros agregados proteicos não-tau. Uma segunda geração tem a vantagem de apresentar uma maior afinidade à proteína tau hiperfosforilada, incluindo nas taupatias primárias.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular neuroimaging in degenerative dementias.Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2013 Sep-Oct;32(5):301-9. doi: 10.1016/j.remn.2013.06.012. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2013. PMID: 23933381 Review. English, Spanish.
-
Cross-validation of biomarkers for the early differential diagnosis and prognosis of dementia in a clinical setting.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016 Mar;43(3):499-508. doi: 10.1007/s00259-015-3170-y. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26341365
-
Impact of (18)FDG PET and (11)C-PIB PET brain imaging on the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias in a regional memory clinic in Hong Kong.Hong Kong Med J. 2016 Aug;22(4):327-33. doi: 10.12809/hkmj154707. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Hong Kong Med J. 2016. PMID: 27313272
-
Frontal variant of Alzheimer's disease with asymmetric presentation mimicking frontotemporal dementia: Case report and literature review.Brain Behav. 2020 Mar;10(3):e01548. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1548. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Brain Behav. 2020. PMID: 31989779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parallel ICA of FDG-PET and PiB-PET in three conditions with underlying Alzheimer's pathology.Neuroimage Clin. 2014 Mar 19;4:508-16. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.03.005. eCollection 2014. Neuroimage Clin. 2014. PMID: 24818077 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Guidelines for the use and interpretation of Alzheimer's disease biomarkers in clinical practice in Brazil: recommendations from the Scientific Department of Cognitive Neurology and Aging of the Brazilian Academy of Neurology.Dement Neuropsychol. 2024 Nov 11;18:e2024C001. doi: 10.1590/1980-5764-DN-2024-C001. eCollection 2024. Dement Neuropsychol. 2024. PMID: 39534442 Free PMC article.
-
How the use of FDG PET is improving the diagnosis of dementia in a reference center in Recife, Brazil.Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2025 May;83(5):1-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0045-1808086. Epub 2025 May 21. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2025. PMID: 40398866 Free PMC article.

