The ethanol extract of Periplaneta Americana L. improves ulcerative colitis induced by a combination of chronic stress and TNBS in rats
- PMID: 35976342
- PMCID: PMC9377204
- DOI: 10.1590/acb370505
The ethanol extract of Periplaneta Americana L. improves ulcerative colitis induced by a combination of chronic stress and TNBS in rats
Abstract
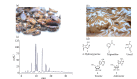
Purpose: To investigate the effects of Periplaneta americana L. on ulcerative colitis (UC) induced by a combination of chronic stress (CS) and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid enema (TNBS) in rats.
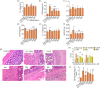
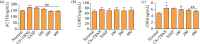
Methods: The experiment UC model with CS was established in rats by a combination of chronic restraint stress, excess failure, improper, and TNBS. The body weight, disease activity index (DAI), colonic mucosal injury index (CMDI), histopathological score (HS) and pro-inflammatory mediators were measured. The content of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) in hypothalamus or adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and corticosteroids (CORT) in plasma were evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The proportion of T lymphocyte subsets was detected by flow cytometry, and gut microbiota was detected by 16S rDNA amplicon sequencing.
Results: Weight loss, DAI, CMDI, HS and proinflammatory mediators were reversed in rats by P. americana L. treatment after UC with CS. Increased epidermal growth factor (EGF) was observed in P. americana L. groups. In addition, P. americana L. could reduce the content of CRH and ACTH and regulate the ratio of CD3+, CD3+CD8+ and CD3+CD4+CD25+/CD4+ in spleen. Comparably, P. americana L. changes composition of gut microbiota.
Conclusions: The ethanol extract of Periplaneta Americana L. improves UC induced by a combination of CS and TNBS in rats.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Nothing to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Eftychi C, Schwarzer R, Vlantis K, Wachsmuth L, Basic M, Wagle P, Neurath MF, Becker C, Bleich A, Pasparakis M. Temporally distinct functions of the cytokines IL-12 and IL-23 drive chronic colon inflammation in response to intestinal barrier impairment. Immunity. 2019;51(2):367–380. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.06.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gao X, Cao Q, Cheng Y, Zhao D, Wang Z, Yang H, Wu Q, You L, Wang Y, Lin Y, Li X, Wang Y, Bian JS, Sun D, Kong L, Birnbaumer L, Yang Y. Chronic stress promotes colitis by disturbing the gut microbiota and triggering immune system response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(13):E2960-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1720696115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brzozowski B, Mazur-Bialy A, Pajdo R, Kwiecien S, Bilski J, Zwolinska-Wcislo M, Mach T, Brzozowski T. Mechanisms by which stress affects the experimental and clinical inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): role of brain-gut axis. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016;14(8):892–900. doi: 10.2174/1570159x14666160404124127. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

