Health-related quality of life of children born very preterm: a multinational European cohort study
- PMID: 35976599
- PMCID: PMC9829588
- DOI: 10.1007/s11136-022-03217-9
Health-related quality of life of children born very preterm: a multinational European cohort study
Abstract
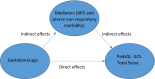
Purpose: This study aims to (1) describe the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) outcomes experienced by children born very preterm (28-31 weeks' gestation) and extremely preterm (< 28 weeks' gestation) at five years of age and (2) explore the mediation effects of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) and severe non-respiratory neonatal morbidity on those outcomes.
Methods: This investigation was based on data for 3687 children born at < 32 weeks' gestation that contributed to the EPICE and SHIPS studies conducted in 19 regions across 11 European countries. Descriptive statistics and multi-level ordinary linear squares (OLS) regression were used to explore the association between perinatal and sociodemographic characteristics and PedsQL™ GCS scores. A mediation analysis that applied generalised structural equation modelling explored the association between potential mediators and PedsQL™ GCS scores.
Results: The multi-level OLS regression (fully adjusted model) revealed that birth at < 26 weeks' gestation, BPD status and experience of severe non-respiratory morbidity were associated with mean decrements in the total PedsQL™ GCS score of 0.35, 3.71 and 5.87, respectively. The mediation analysis revealed that the indirect effects of BPD and severe non-respiratory morbidity on the total PedsQL™ GCS score translated into decrements of 1.73 and 17.56, respectively, at < 26 weeks' gestation; 0.99 and 10.95, respectively, at 26-27 weeks' gestation; and 0.34 and 4.80, respectively, at 28-29 weeks' gestation (referent: birth at 30-31 weeks' gestation).
Conclusion: The findings suggest that HRQoL is particularly impaired by extremely preterm birth and the concomitant complications of preterm birth such as BPD and severe non-respiratory morbidity.
Keywords: Children; Mediation analysis; PedsQL; Preterm birth; health-related quality of life.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Arpino C, et al. Preterm birth and neurodevelopmental outcome: A review. Child’s nervous system. 2010;26(9):1139–1149. - PubMed
-
- CDC. Preterm birth. 2021 [cited 21 Oct 2021]; Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/maternalinfanthealth/pretermbirth....
-
- Larroque B, et al. Neurodevelopmental disabilities and special care of 5-year-old children born before 33 weeks of gestation (the EPIPAGE study): A longitudinal cohort study. The Lancet. 2008;371(9615):813–820. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources