N-Heterocyclic Carbene Modified Palladium Catalysts for the Direct Synthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide
- PMID: 35976628
- PMCID: PMC9449981
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c04828
N-Heterocyclic Carbene Modified Palladium Catalysts for the Direct Synthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide
Abstract
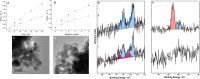
Heterogeneous palladium catalysts modified by N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) are shown to be highly effective toward the direct synthesis of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), in the absence of the promoters which are typically required to enhance both activity and selectivity. Catalytic evaluation in a batch regime demonstrated that through careful selection of the N-substituent of the NHC it is possible to greatly enhance catalytic performance when compared to the unmodified analogue and reach concentrations of H2O2 rivaling that obtained by state-of-the-art catalysts. The enhanced performance of the modified catalyst, which is retained upon reuse, is attributed to the ability of the NHC to electronically modify Pd speciation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

