De novo variants in genes regulating stress granule assembly associate with neurodevelopmental disorders
- PMID: 35977029
- PMCID: PMC9385150
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abo7112
De novo variants in genes regulating stress granule assembly associate with neurodevelopmental disorders
Abstract
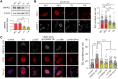
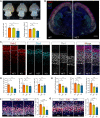
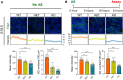
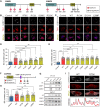
Stress granules (SGs) are cytoplasmic assemblies in response to a variety of stressors. We report a new neurodevelopmental disorder (NDD) with common features of language problems, intellectual disability, and behavioral issues caused by de novo likely gene-disruptive variants in UBAP2L, which encodes an essential regulator of SG assembly. Ubap2l haploinsufficiency in mouse led to social and cognitive impairments accompanied by disrupted neurogenesis and reduced SG formation during early brain development. On the basis of data from 40,853 individuals with NDDs, we report a nominally significant excess of de novo variants within 29 genes that are not implicated in NDDs, including 3 essential genes (G3BP1, G3BP2, and UBAP2L) in the core SG interaction network. We validated that NDD-related de novo variants in newly implicated and known NDD genes, such as CAPRIN1, disrupt the interaction of the core SG network and interfere with SG formation. Together, our findings suggest the common SG pathology in NDDs.
Figures



References
-
- Parenti I., Rabaneda L. G., Schoen H., Novarino G., Neurodevelopmental disorders: From genetics to functional pathways. Trends Neurosci. 43, 608–621 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Satterstrom F. K., Kosmicki J. A., Wang J., Breen M. S., De Rubeis S., An J. Y., Peng M., Collins R., Grove J., Klei L., Stevens C., Reichert J., Mulhern M. S., Artomov M., Gerges S., Sheppard B., Xu X., Bhaduri A., Norman U., Brand H., Schwartz G., Nguyen R., Guerrero E. E., Dias C.; Autism Sequencing Consortium; iPSYCH-Broad Consortium, Betancur C., Cook E. H., Gallagher L., Gill M., Sutcliffe J. S., Thurm A., Zwick M. E., Borglum A. D., State M. W., Cicek A. E., Talkowski M. E., Cutler D. J., Devlin B., Sanders S. J., Roeder K., Daly M. J., Buxbaum J. D., Large-scale exome sequencing study implicates both developmental and functional changes in the neurobiology of autism. Cell 180, 568–584.e23 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coe B. P., Stessman H. A. F., Sulovari A., Geisheker M. R., Bakken T. E., Lake A. M., Dougherty J. D., Lein E. S., Hormozdiari F., Bernier R. A., Eichler E. E., Neurodevelopmental disease genes implicated by de novo mutation and copy number variation morbidity. Nat. Genet. 51, 106–116 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kaplanis J., Samocha K. E., Wiel L., Zhang Z., Arvai K. J., Eberhardt R. Y., Gallone G., Lelieveld S. H., Martin H. C., McRae J. F., Short P. J., Torene R. I., de Boer E., Danecek P., Gardner E. J., Huang N., Lord J., Martincorena I., Pfundt R., Reijnders M. R. F., Yeung A., Yntema H. G.; Deciphering Developmental Disorders Study, Vissers L., Juusola J., Wright C. F., Brunner H. G., Firth H. V., FitzPatrick D. R., Barrett J. C., Hurles M. E., Gilissen C., Retterer K., Evidence for 28 genetic disorders discovered by combining healthcare and research data. Nature 586, 757–762 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arlotta P., Molyneaux B. J., Chen J., Inoue J., Kominami R., Macklis J. D., Neuronal subtype-specific genes that control corticospinal motor neuron development in vivo. Neuron 45, 207–221 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

