Trends in US Medicare Decedents' Diagnosis of Dementia From 2004 to 2017
- PMID: 35977316
- PMCID: PMC8976239
- DOI: 10.1001/jamahealthforum.2022.0346
Trends in US Medicare Decedents' Diagnosis of Dementia From 2004 to 2017
Abstract
Importance: Alzheimer disease and related dementias (ADRD) have received considerable attention among clinicians, researchers, and policy makers in recent years. Despite increased awareness, few studies have documented temporal changes in the documentation of ADRD diagnoses despite its new importance for risk adjustment for health plans in Medicare.
Objective: To assess trends in frequency of ADRD diagnosis in the last 2 years of life from 2004 to 2017, as well as any associated changes in billing practices, characteristics of the population with diagnosed ADRD, and intensity of end-of-life care.
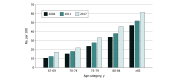
Design setting and participants: This is a serial cross-sectional study of older adult decedents (67 years or older) from 2004 to 2017 using a 20% sample of fee-for-service Medicare decedents. An ADRD diagnosis within the last 2 years of life was identified using diagnosis codes from inpatient, professional service, home health, or hospice claims, requiring the standard claims algorithm that required at least 1 claim and a more stringent algorithm that required at least 2 claims. Trends in ADRD diagnosis among decedents were used to lessen influence of new diagnostic technologies for early stage disease. Demographic characteristics, selected comorbidities, place of death, and health service use at the end-of-life were also examined. Data were analyzed from July 9, 2020, to May 3, 2021.
Exposures: Calendar year 2004 to 2017.
Main outcome and measure: An ADRD diagnosis within 2 years of death.
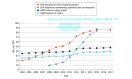
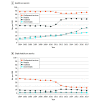
Results: Among the included 3 515 329 Medicare fee-for-service decedents, when adjusted for age and sex, the percentage of older decedents with an ADRD diagnosis increased from 34.7% in 2004 to 47.2% in 2017. The trend was attenuated (25.2% to 39.2%) using a stringent ADRD definition. There was an inflection in the curve from 2011 to 2013, the time at which additional diagnoses were added to Medicare claims and the National Alzheimer Care Act was enacted. The ADRD diagnosis frequency increased considerably in inpatient (49.0% to 67.3%), hospice (12.2% to 42.0%), and home health (10.1% to 28.7%) claims. However, individual characteristics, number of visits, and hospitalizations were similar across the study period, and the intensity of end-of-life care declined on most measures.
Conclusions and relevance: In this cross-sectional study, nearly half of older Medicare decedents had a diagnosis of ADRD at the time of death. From 2004 to 2017, the percentage of older adult decedents who received an ADRD diagnosis increased substantially prior to announcement of the addition of ADRD to Medicare risk adjustment strategies.
Copyright 2022 Davis MA et al. JAMA Health Forum.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: Dr Davis reported personal fees from Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine for statistical review outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

