Electrochemical paper-based antigen sensing platform using plant-derived monoclonal antibody for detecting SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 35977451
- PMCID: PMC9357285
- DOI: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123783
Electrochemical paper-based antigen sensing platform using plant-derived monoclonal antibody for detecting SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
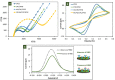
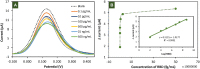
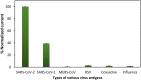
The current approaches of diagnostic platforms for detecting SARS-CoV-2 infections mostly relied on adapting the existing technology. In this work, a simple and low-cost electrochemical sensing platform for detecting SAR-CoV-2 antigen was established. The proposed sensor combined the innovative disposable paper-based immunosensor and cost-effective plant-based anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody CR3022, expressed in Nicotiana benthamiana. The cellulose nanocrystal was modified on screen-printed graphene electrode to provide the abundant COOH functional groups on electrode surface, leading to the high ability for antibody immobilization. The quantification of the presence receptor binding domain (RBD) spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 was performed using differential pulse voltammetry by monitoring the changing current of [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- redox solution. The current change of [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- before and after the presence of target RBD could be clearly distinguished, providing a linear relationship with RBD concentration in the range from 0.1 pg/mL to 500 ng/mL with the minimum limit of detection of 2.0 fg/mL. The proposed platform was successfully applied to detect RBD in nasopharyngeal swab samples with satisfactory results. Furthermore, the paper-based immunosensor was extended to quantify the RBD level in spiked saliva samples, demonstrating the broadly applicability of this system. This electrochemical paper-based immunosensor has the potential to be employed as a point-of-care testing for COVID-19 diagnosis.
Keywords: Differential pulse voltammetry; Paper-based electrochemical immunosensor; Plant-based antibody; Point-of-care; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- sprinklr WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. 2022. https://covid19.who.int Accessed May 14 2022.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

