Vitamin E functions by association with a novel binding site on the 67 kDa laminin receptor activating diacylglycerol kinase
- PMID: 35977663
- PMCID: PMC10243646
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2022.109129
Vitamin E functions by association with a novel binding site on the 67 kDa laminin receptor activating diacylglycerol kinase
Abstract
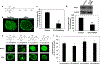
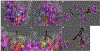
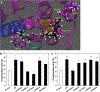
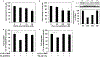
It is generally recognized that the main function of α-tocopherol (αToc), which is the most active form of vitamin E, is its antioxidant effect, while non-antioxidant effects have also been reported. We previously found that αToc ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via diacylglycerol kinase alpha (DGKα) activation in vivo, and the activation was not related to the antioxidant effect. However, the underlying mechanism of how αToc activates DGKα have been enigmatic. We report that the membrane-bound 67 kDa laminin receptor (67LR), which has previously been shown to serve as a receptor for epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), also contains a novel binding site for vitamin E, and its association with Vitamin E mediates DGKα activation by αToc. We employed hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX/MS) and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to identify the specific binding site of αToc on the 67LR and discovered the conformation of the specific hydrophobic pocket that accommodates αToc. Also, HDX/MS and MD simulations demonstrated the detailed binding of EGCG to a water-exposed hydrophilic site on 67LR, while in contrast αToc binds to a distinct hydrophobic site. We demonstrated that 67LR triggers an important signaling pathway mediating non-antioxidant effects of αToc, such as DGKα activation. This is the first evidence demonstrating a membrane receptor for αToc and one of the underlying mechanisms of a non-antioxidant function for αToc.
Keywords: 67 kDa laminin receptor; diabetic nephrophaty; diacylglycerol kinase; epigallocatechin gallate; vitamin E.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
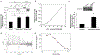
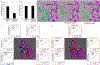

Similar articles
-
Epigallocatechin Gallate Induces Upregulation of LDL Receptor via the 67 kDa Laminin Receptor-Independent Pathway in HepG2 Cells.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020 Apr;64(7):e1901036. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201901036. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020. PMID: 31978263
-
Amelioration of diabetic nephropathy by oral administration of d-α-tocopherol and its mechanisms.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2018 Jan;82(1):65-73. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2017.1411184. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29297254
-
The mechanisms of ameliorating effect of a green tea polyphenol on diabetic nephropathy based on diacylglycerol kinase α.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 16;10(1):11790. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68716-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32678222 Free PMC article.
-
67-kDa Laminin Receptor-Mediated Cellular Sensing System of Green Tea Polyphenol EGCG and Functional Food Pairing.Molecules. 2022 Aug 11;27(16):5130. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165130. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36014370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular basis for cancer chemoprevention by green tea polyphenol EGCG.Forum Nutr. 2009;61:156-169. doi: 10.1159/000212748. Epub 2009 Apr 7. Forum Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19367120 Review.
Cited by
-
Flavonoid quercetin and its glucuronide and sulfate conjugates bind to 67-kDa laminin receptor and prevent neuronal cell death induced by serum starvation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023 Sep 3;671:116-123. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.06.007. Epub 2023 Jun 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 37300941 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol and its metabolites elicit neuroprotection via high-affinity binding to the laminin receptor at low nanomolar concentrations.FEBS Lett. 2024 May;598(9):995-1007. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14835. Epub 2024 Feb 27. FEBS Lett. 2024. PMID: 38413095 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Diacylglycerol Kinase in the Amelioration of Diabetic Nephropathy.Molecules. 2022 Oct 11;27(20):6784. doi: 10.3390/molecules27206784. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36296376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Obesity and Anti-Inflammatory Synergistic Effects of Green Tea Catechins and Citrus β-Cryptoxanthin Ingestion in Obese Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 11;24(8):7054. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087054. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108217 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection by resveratrol-glucuronide and quercetin-glucuronide via binding to polyphenol- and glycosaminoglycan-binding sites in the laminin receptor.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Mar 1;20(3):819-820. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00160. Epub 2024 May 17. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38886954 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Azzi A, Stocker A. Vitamin E : non-antioxidant roles 2000;39:231–55. - PubMed
-
- Tasinato A, Boscoboinik D, Bartoli GM, Maroni P, Azzi A. d-α-tocopherol inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation occurs at physiological concentrations, correlates with protein kinase C inhibition, and is independent of its antioxidant properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1995;92:12190–4. 10.1073/pnas.92.26.12190. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

