Novel prime-boost immune-based therapy inhibiting both hepatitis B and D virus infections
- PMID: 35977815
- PMCID: PMC10176361
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327216
Novel prime-boost immune-based therapy inhibiting both hepatitis B and D virus infections
Abstract
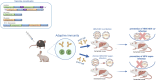
Objective: Chronic HBV/HDV infections are a major cause of liver cancer. Current treatments can only rarely eliminate HBV and HDV. Our previously developed preS1-HDAg immunotherapy could induce neutralising antibodies to HBV in vivo and raise HBV/HDV-specific T-cells. Here, we further investigate if a heterologous prime-boost strategy can circumvent T-cell tolerance and preclude HDV superinfection in vivo.
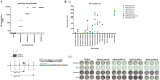
Design: A DNA prime-protein boost strategy was evaluated for immunogenicity in mice and rabbits. Its ability to circumvent T-cell tolerance was assessed in immunocompetent hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)-transgenic mice. Neutralisation of HBV and HDV was evaluated both in vitro and in immunodeficient human-liver chimeric mice upon adoptive transfer.
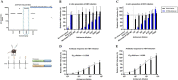
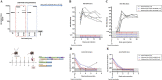
Results: The prime-boost strategy elicits robust HBV/HDV-specific T-cells and preS1-antibodies that can effectively prevent HBV and HDV (co-)infection in vitro and in vivo. In a mouse model representing the chronic HBsAg carrier state, active immunisation primes high levels of preS1-antibodies and HDAg-specific T-cells. Moreover, transfer of vaccine-induced antibodies completely protects HBV-infected human-liver chimeric mice from HDV superinfection.
Conclusion: The herein described preS1-HDAg immunotherapy is shown to be immunogenic and vaccine-induced antibodies are highly effective at preventing HBV and HDV (super)infection both in vitro and in vivo. Our vaccine can complement current and future therapies for the control of chronic HBV and HDV infection.
Keywords: antiviral therapy; chronic viral hepatitis; hepatitis B; hepatitis D; immunotherapy.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MS and LF are founders and shareholders of Svenska Vaccinfabriken, which holds the IP to the immunogens described in this manuscript. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures

Comment in
-
Prophylactic vaccination against hepatitis D virus superinfection: from fiction to reality?Gut. 2023 Jun;72(6):1030-1032. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-328381. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Gut. 2023. PMID: 36261292 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Blocking Entry of Hepatitis B and D Viruses to Hepatocytes as a Novel Immunotherapy for Treating Chronic Infections.J Infect Dis. 2021 Jan 4;223(1):128-138. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa036. J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 31994701 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives for a vaccine against hepatitis delta virus.Semin Liver Dis. 2012 Aug;32(3):256-61. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1323631. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Semin Liver Dis. 2012. PMID: 22932974 Review.
-
Ubiquitinated Hepatitis D Antigen-Loaded Microvesicles Induce a Potent Specific Cellular Immune Response to Inhibit HDV Replication in Vivo.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0102421. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01024-21. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34908456 Free PMC article.
-
Humanized chimeric uPA mouse model for the study of hepatitis B and D virus interactions and preclinical drug evaluation.Hepatology. 2012 Mar;55(3):685-94. doi: 10.1002/hep.24758. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22031488
-
Future treatments for hepatitis delta virus infection.Liver Int. 2020 Feb;40 Suppl 1:54-60. doi: 10.1111/liv.14356. Liver Int. 2020. PMID: 32077603 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced antibody response to the conformational non-RBD region via DNA prime-protein boost elicits broad cross-neutralization against SARS-CoV-2 variants.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025 Dec;14(1):2447615. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2447615. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025. PMID: 39727342 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles of vaccine-induced SARS-CoV-2-specific neutralizing antibodies and T cells in protection and disease.Mol Ther. 2024 Feb 7;32(2):540-555. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.01.007. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38213030 Free PMC article.
-
Mixed formulation of mRNA and protein-based COVID-19 vaccines triggered superior neutralizing antibody responses.MedComm (2020). 2022 Dec 2;3(4):e188. doi: 10.1002/mco2.188. eCollection 2022 Dec. MedComm (2020). 2022. PMID: 36474858 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous Prime-Boost Immunization Strategies Using Varicella-Zoster Virus gE mRNA Vaccine and Adjuvanted Protein Subunit Vaccine Triggered Superior Cell Immune Response in Middle-Aged Mice.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Aug 6;19:8029-8042. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S464720. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39130684 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential Immunization with Vaccines Based on SARS-CoV-2 Virus-like Particles Induces Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Aug 19;12(8):927. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12080927. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204050 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
