Hospital mortality and prognostic factors in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury and cancer undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy
- PMID: 35977906
- PMCID: PMC9731773
- DOI: 10.23876/j.krcp.21.305
Hospital mortality and prognostic factors in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury and cancer undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy
Abstract
Background: Whether continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) should be applied to critically ill patients with both acute kidney injury (AKI) and cancer remains controversial because of poor expected outcomes. The present study determined prognostic factors for all-cause in-hospital mortality in patients with AKI and cancer undergoing CRRT.
Methods: We included 471 patients with AKI and cancer who underwent CRRT at the intensive care unit of a Korean tertiary hospital from 2013 to 2020, and classified them by malignancy type. The primary outcomes were 28-day all-cause mortality rate and prognostic factors for in-hospital mortality. The secondary outcome was renal replacement therapy (RRT) dependency at hospital discharge.
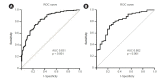
Results: The 28-day mortality rates were 58.8% and 82% in the solid and hematologic malignancy groups, respectively. Body mass index (BMI), presence of oliguria, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score, and albumin level were common predictors of 28-day mortality in the solid and hematologic malignancy groups. A high heart rate and the presence of severe acidosis were prognostic factors only in the solid malignancy group. Among the survivors, the proportion with RRT dependency was 25.0% and 33.3% in the solid and hematologic malignancy groups, respectively.
Conclusion: The 28-day mortality rate of cancer patients with AKI undergoing CRRT was high in both the solid and hematologic malignancy groups. BMI, presence of oliguria, SOFA score, and albumin level were common predictors of 28-day mortality in the solid and hematologic malignancy groups, but a high heart rate and severe acidosis were prognostic factors only in the solid malignancy group.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Continuous renal replacement therapy; Malignancy.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- van Vliet M, Verburg IW, van den Boogaard M, et al. Trends in admission prevalence, illness severity and survival of haematological patients treated in Dutch intensive care units. Intensive Care Med. 2014;40:1275–1284. - PubMed
-
- Benoit DD, Hoste EA. Acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with cancer. Crit Care Clin. 2010;26:151–179. - PubMed
-
- Libório AB, Abreu KL, Silva GB, Jr, et al. Predicting hospital mortality in critically ill cancer patients according to acute kidney injury severity. Oncology. 2011;80:160–166. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

