Puerarin ameliorates acute lung injury by modulating NLRP3 inflammasome-induced pyroptosis
- PMID: 35977927
- PMCID: PMC9385627
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-022-01137-8
Puerarin ameliorates acute lung injury by modulating NLRP3 inflammasome-induced pyroptosis
Abstract
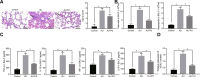
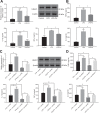
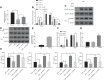
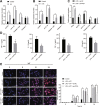
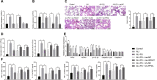
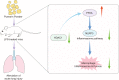
We commenced to analyze putative anti-pyroptosis effects of puerarin (PU) as mediated by the PP2A-HDAC1-NLRP3 pathway in acute lung injury (ALI). ALI animal and cell models were constructed, followed by treatment of PU. Then, the effect of HDAC1, PP2A, and NLRP3 on cell inflammation and pyroptosis was explored. The interaction between HDAC1 and PP2A as well as between PP2A and NLRP3 was analyzed. Our findings suggested that PU downregulated HDAC1 expression to alleviate symptoms of ALI. HDAC1 overexpression promoted inflammation induced by LPS, which reversed the inhibitory effect of PU on ALI. HDAC1 overexpression also decreased PP2A expression, suggesting that PP2A was involved in the effects of HDAC1 on LPS-induced inflammation. PP2A exerted inhibitory effects on NLRP3. Meanwhile, PU hindered the progression of ALI by silencing HDAC1 or overexpressing PP2A both in vivo and in vitro. Taken together, PU restrained pyroptosis of cells induced by NLRP3 inflammasome to abate ALI.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

