Prognostic values of high sensitivity cardiac troponin T and I for long-term mortality in hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 35977974
- PMCID: PMC9386012
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-17799-4
Prognostic values of high sensitivity cardiac troponin T and I for long-term mortality in hemodialysis patients
Abstract
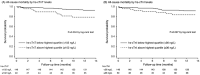
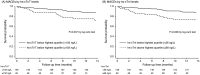
Previous studies using contemporary cardiac troponin (cTn) assays have shown conflicting results in predictability of mortality and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) in hemodialysis patients. We aimed to evaluate the prognostic values of high-sensitivity cTnT (hs-cTnT) and hs-cTnI for long-term mortality and MACEs in asymptomatic chronic hemodialysis patients. 198 asymptomatic patients undergoing regular hemodialysis (age 62.4 ± 14.8 years) were enrolled. Pre-dialysis hs-cTnT and hs-cTnI levels were measured. The study outcomes were long-term all-cause mortality and MACEs. Median values of hs-cTnT and hs-cTnI were 61.1 ng/L (IQR 36.6-102.0) and 18.4 ng/L (IQR 9.5-36.6), respectively. During a median follow-up of 13.5 months, 30 (15.1%) patients developed MACEs, and 20 (10.1%) patients died. The patients in highest quartile of hs-cTnT level (≥ 102 ng/L) had increased risk of long-term mortality (HR 3.34; 95%CI 1.39-8.04, P = 0.005). However, hs-cTnI levels above highest quartile (≥ 36 ng/L) was not significantly associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality. Nevertheless, elevated level of hs-cTnT and hs-cTnI was associated with increased risk of MACEs. We demonstrated that higher level of hs-cTnT, but not hs-cTnI, was associated with increased risk of long-term mortality. Nevertheless, higher level of hs-cTnT and hs-cTnI both were associated with greater risk of long-term MACEs.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous