MARTX toxin of Vibrio vulnificus induces RBC phosphatidylserine exposure that can contribute to thrombosis
- PMID: 35978022
- PMCID: PMC9385741
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32599-0
MARTX toxin of Vibrio vulnificus induces RBC phosphatidylserine exposure that can contribute to thrombosis
Abstract
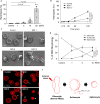
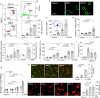
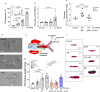
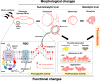
V. vulnificus-infected patients suffer from hemolytic anemia and circulatory lesions, often accompanied by venous thrombosis. However, the pathophysiological mechanism of venous thrombosis associated with V. vulnificus infection remains largely unknown. Herein, V. vulnificus infection at the sub-hemolytic level induced shape change of human red blood cells (RBCs) accompanied by phosphatidylserine exposure, and microvesicle generation, leading to the procoagulant activation of RBCs and ultimately, acquisition of prothrombotic activity. Of note, V. vulnificus exposed to RBCs substantially upregulated the rtxA gene encoding multifunctional autoprocessing repeats-in-toxin (MARTX) toxin. Mutant studies showed that V. vulnificus-induced RBC procoagulant activity was due to the pore forming region of the MARTX toxin causing intracellular Ca2+ influx in RBCs. In a rat venous thrombosis model triggered by tissue factor and stasis, the V. vulnificus wild type increased thrombosis while the ΔrtxA mutant failed to increase thrombosis, confirming that V. vulnificus induces thrombosis through the procoagulant activation of RBCs via the mediation of the MARTX toxin.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sun, Y., Lin, Y. Z. & Chen, Z. G. An uncommon case of necrotizing fasciitis and septic shock caused by Vibrio vulnificus infection–related freshwater shrimp stung. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 1534734620973992 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC Vibrio vulnificus infections associated with eating raw oysters–Los Angeles, 1996. MMWR. 1996;45:621–624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

