Post-translational control of beige fat biogenesis by PRDM16 stabilization
- PMID: 35978186
- PMCID: PMC9433319
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05067-4
Post-translational control of beige fat biogenesis by PRDM16 stabilization
Abstract
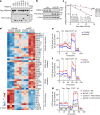
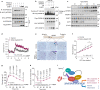
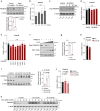
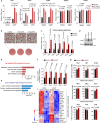
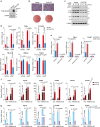
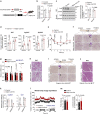
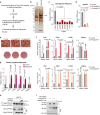
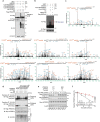
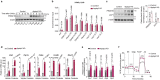
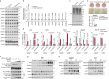
Compelling evidence shows that brown and beige adipose tissue are protective against metabolic diseases1,2. PR domain-containing 16 (PRDM16) is a dominant activator of the biogenesis of beige adipocytes by forming a complex with transcriptional and epigenetic factors and is therefore an attractive target for improving metabolic health3-8. However, a lack of knowledge surrounding the regulation of PRDM16 protein expression hampered us from selectively targeting this transcriptional pathway. Here we identify CUL2-APPBP2 as the ubiquitin E3 ligase that determines PRDM16 protein stability by catalysing its polyubiquitination. Inhibition of CUL2-APPBP2 sufficiently extended the half-life of PRDM16 protein and promoted beige adipocyte biogenesis. By contrast, elevated CUL2-APPBP2 expression was found in aged adipose tissues and repressed adipocyte thermogenesis by degrading PRDM16 protein. Importantly, extended PRDM16 protein stability by adipocyte-specific deletion of CUL2-APPBP2 counteracted diet-induced obesity, glucose intolerance, insulin resistance and dyslipidaemia in mice. These results offer a cell-autonomous route to selectively activate the PRDM16 pathway in adipose tissues.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Comment in
-
PRDM16 stability and metabolically healthy adipose tissue.Nat Metab. 2022 Sep;4(9):1095-1096. doi: 10.1038/s42255-022-00639-0. Nat Metab. 2022. PMID: 36064603 No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK075787/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK133948/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK127575/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125283/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32 DK007516/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK135043/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD028635/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK097441/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125281/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- K99 DK127196/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

