Antibacterial activity of recently approved antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35978400
- PMCID: PMC9382732
- DOI: 10.1186/s12941-022-00529-z
Antibacterial activity of recently approved antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections are considered an important public health problem, and treatment options are limited. Accordingly, in this meta-analysis, we analyzed published studies to survey in vitro activity of recently approved antibiotics against MRSA isolates.
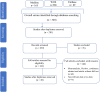
Methods: We searched electronic databases; PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science to identify relevant studies (until November 30, 2020) that have focused on the in vitro activity of telavancin, dalbavancin, oritavancin, and tedizolid against MRSA isolates. Statistical analyses were conducted using STATA software (version 14.0).
Results: Thirty-eight studies were included in this meta-analysis. Overall in vitro activity of tedizolid on 12,204 MRSA isolates was 0.250 and 0.5 µg/mL for MIC50 and MIC90, (minimum inhibitory concentration at which 50% and 90% of isolates were inhibited, respectively), respectively. The overall antibacterial activity of dalbavancin on 28539 MRSA isolates was 0.060 and 0.120 µg/mL for MIC50 and MIC90, respectively. The overall antibacterial activity of oritavancin on 420 MRSA isolates was 0.045 and 0.120 µg/mL for MIC50 and MIC90, respectively. The overall antibacterial activity of telavancin on 7353 MRSA isolates was 0.032 and 0.060 µg/mL for MIC50 and MIC90, respectively. The pooled prevalence of tedizolid, telavancin, and dalbavancin susceptibility was 100% (95% CI: 100-100).
Conclusion: Telavancin, dalbavancin, oritavancin, and tedizolid had potent in vitro activity against MRSA isolates. The low MICs and high susceptibility rates of these antibiotics recommend a hopeful direction to introduce useful antibiotics in treating MRSA infections in the future.
Keywords: Antibacterial activity; Dalbavancin; Lipoglycopeptide; MRSA; Oritavancin; Tedizolid; Telavancin.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibacterial and antibiofilm potentials of vancomycin-loaded niosomal drug delivery system against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections.BMC Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 8;24(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12896-024-00874-1. BMC Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38978013 Free PMC article.
-
Newer glycopeptide antibiotics for treatment of complicated skin and soft tissue infections: systematic review, network meta-analysis and cost analysis.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018 Apr;24(4):361-368. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2017.08.028. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018. PMID: 28882727 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, trend and antimicrobial susceptibility of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Nigeria: a systematic review.J Infect Public Health. 2018 Nov-Dec;11(6):763-770. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2018.05.013. Epub 2018 Jun 19. J Infect Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29933910
-
Simulated exposures of oritavancin in in vitro pharmacodynamic models select for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility to oritavancin but minimal cross-resistance or seesaw effect with other antimicrobials.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025 Apr 2;80(4):1108-1115. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaf042. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025. PMID: 39936452
-
Proportions of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in patients with surgical site infections in mainland China: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 20;10(1):e0116079. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116079. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25602284 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Clinical Efficacy of Multidose Oritavancin: A Systematic Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Sep 29;12(10):1498. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12101498. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of genetic mutations conferring tedizolid resistance in MRSA mutants.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025 Aug;44(8):1917-1924. doi: 10.1007/s10096-025-05157-x. Epub 2025 May 13. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40360924 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and antibiofilm potentials of vancomycin-loaded niosomal drug delivery system against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections.BMC Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 8;24(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12896-024-00874-1. BMC Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38978013 Free PMC article.
-
MRSA: the enduring foe.Infect Prev Pract. 2025 Mar 25;7(2):100459. doi: 10.1016/j.infpip.2025.100459. eCollection 2025 Jun. Infect Prev Pract. 2025. PMID: 40525117 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Modulation of the Gut Microbiota by the Plantaricin-Producing Lactiplantibacillus plantarum D13, Analysed in the DSS-Induced Colitis Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 18;24(20):15322. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015322. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895001 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rajput A, Poudel S, Tsunemoto H, Meehan M, Szubin R, Olson CA, Seif Y, Lamsa A, Dillon N, Vrbanac A. Identifying the effect of vancomycin on health care–associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains using bacteriological and physiological media. GigaScience. 2021;10(1):giaa156. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giaa156. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Panwala T, Gandhi P, Jethwa D: Inducible Clindamycin resistance and MRSA amongst Staphylococcus aureus isolates: A phenotypic detection.
-
- Thabit AK, Nicolau DP, Kuti JL. In vitro pharmacodynamics of human simulated exposures of telavancin against methicillin-susceptible and-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with and without prior vancomycin exposure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(1):222–228. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02033-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical