Lamprey immune protein triggers the ferroptosis pathway during zebrafish embryonic development
- PMID: 35978430
- PMCID: PMC9386916
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-022-00933-0
Lamprey immune protein triggers the ferroptosis pathway during zebrafish embryonic development
Abstract
Background: Previously, a novel lamprey immune protein (LIP) was identified, which plays an important role in immunity and the regulation of growth and development in lampreys. However, the mechanism of how LIP regulates growth and development remains unclear.
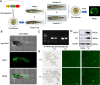
Methods: In this study, a zebrafish model of LIP overexpression was established by delivering a transgenic plasmid to the fertilized egg. The biological function of LIP was explored in vivo through phenotypic characterization, comparative transcriptome sequencing, and physiological and biochemical analyses.
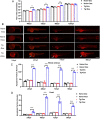
Results: LIP caused developmental toxicity in zebrafish, increased embryo mortality and exhibited strong teratogenic, lethal, and developmental inhibitory effects. Comparative transcriptome analysis showed that LIP-induced large-scale cell death by triggering ferroptosis. Furthermore, LIP-induced lipid peroxidation and caused pericardial edema. Direct inhibition of acsl4a and tfr1a, or silencing of acsl4a and tfr1a with specific siRNA suppressed ferroptosis and pericardial edema.
Conclusions: Taken together, we confirmed that LIP can participate in growth and development via the regulation of lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. This lays the foundation for future studies on the function of LIP in lampreys. Video Abstract.
Keywords: Edema; Ferroptosis; LIP; Lipid peroxidation; Transgenic zebrafish.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

