Design, synthesis, anticancer evaluation and docking studies of novel 2-(1-isonicotinoyl-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-3-phenylthiazolidin-4-one derivatives as Aurora-A kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 35978438
- PMCID: PMC9382805
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-022-00852-8
Design, synthesis, anticancer evaluation and docking studies of novel 2-(1-isonicotinoyl-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-3-phenylthiazolidin-4-one derivatives as Aurora-A kinase inhibitors
Abstract
Introduction: Aurora-A kinase is associated with the Aurora kinase family which has been considered a striking anticancer target for the treatment of human cancers.
Objective: To design, synthesize, anticancer evaluation, and docking studies of novel 2-(1-isonicotinoyl-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-3-phenylthiazolidin-4-one derivatives as Aurora-A Kinase inhibitors.
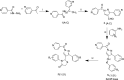
Method: A total of 21 Pyrazole derivatives P (1-21) were synthesized by using the Vilsmeier Haack reagent which was characterized by FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and Mass spectroscopy. The synthesized derivatives were evaluated for their potential in vitro anticancer activity by MTT assay and Aurora-A kinase inhibition assay.
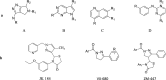
Results: The cytotoxicity assay (MTT assay) showed that compound P-6 exhibited potent cytotoxicity (IC50 = 0.37-0.44 μM) against two cancer (HCT 116 and MCF-7) cell lines, which were comparable to the standard compound, VX-680. Compound P-6 also showed inhibition of Aurora-A kinase with an IC50 value of 0.11 ± 0.03 µM. A Docking study was done to compound P-6 and P-20 into the active site of Aurora A kinase, in order to get the probable binding model for further study.
Conclusion: A series of 21 novel pyrazole derivatives P(1-21) were designed, synthesized, in vitro anticancer evaluation, and docking studies for Aurora A kinase inhibition. The results established that P-6 is a prospective aspirant for the development of anticancer agents targeting Aurora-A kinase.
Keywords: Aurora-A kinase; Cell cycle arrest; Docking studies; MTT assay; Pyrazole; Thiazolidin-4-one.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, biological activity evaluation of 3-(4-phenyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole derivatives as potent JAK 2/3 and aurora A/B kinases multi-targeted inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Jan 1;209:112934. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112934. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33109396
-
Design, synthesis, biological evaluation of 6-(2-amino-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-6-yl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one derivatives as novel anticancer agents with Aurora kinase inhibition.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Mar 15;190:112108. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112108. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32058239
-
A novel class of pyrazole analogues as aurora kinase A inhibitor: design, synthesis, and anticancer evaluation.Bioorg Chem. 2023 Dec;141:106901. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106901. Epub 2023 Oct 1. Bioorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 37797455
-
Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular docking studies of N,1,3-triphenyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide derivatives as anticancer agents.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Jun 1;22(11):3589-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.04.066. Epub 2012 Apr 21. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 22572580
-
Novel benzothiazole-based dual VEGFR-2/EGFR inhibitors targeting breast and liver cancers: Synthesis, cytotoxic activity, QSAR and molecular docking studies.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022 Feb 15;58:128529. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128529. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35007724 Review.
Cited by
-
2-Substituted-3-(5-Substituted-1,3,4-oxadiazol/thiadiazol-2-yl) Thiazolidin-4-one Derivatives: Synthesis, Anticancer, Antimicrobial, and Antioxidant Potential.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 29;16(6):805. doi: 10.3390/ph16060805. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375752 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, Anticancer, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Potential of Novel 4-(Substituted phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol/thiadiazol-2-yl)-4-(4-substituted phenyl) Azetidin-2-One Derivatives.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Mar 30;16(4):517. doi: 10.3390/ph16040517. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111274 Free PMC article.
-
Salsoline derivatives, genistein, semisynthetic derivative of kojic acid, and naringenin as inhibitors of A42R profilin-like protein of monkeypox virus: in silico studies.Front Chem. 2024 Sep 10;12:1445606. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1445606. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 39318419 Free PMC article.
-
Trilliumosides K and L, two novel steroidal saponins from rhizomes of Trillium govanianum, as potent anti-cancer agents targeting apoptosis in the A-549 cancer cell line.Front Chem. 2023 Dec 22;11:1306271. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1306271. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 38188932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Workman P, Kaye S. Translating Basic Cancer Research into new cancer therapeutics. Trends Mol Med. 2002;8:1. - PubMed
-
- Chabner BA, Roberts TG., Jr Timeline: chemotherapy and the war on cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:65–72. - PubMed
-
- Pellegrini F, Budman DR. Review: tubulin function, action of antitubulin drugs, and new drug development. Cancer Invest. 2005;23:264–273. - PubMed
-
- Hansen JD, Grina J, Newhouse B, Welch M, Topalov G, Littman N. Potent and selective pyrazole-based inhibitors of B-Rafkinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008;18(16):4692–4695. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
