Impact of ANN in Revealing of Viral Peptides
- PMID: 35978632
- PMCID: PMC9377878
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7760734
Impact of ANN in Revealing of Viral Peptides
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Impact of ANN in Revealing of Viral Peptides.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Dec 29;2023:9835650. doi: 10.1155/2023/9835650. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 38188747 Free PMC article.
Abstract
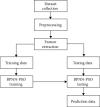
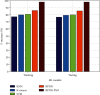
All organisms contain antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), which are a critical component of the innate immune system. These chemicals have the ability to suppress the growth of a variety of fungi, bacteria, and viruses. Because AMPs interact with structural components of the microbial cell membrane and have a wide range of cellular targets, bacteria are unlikely to be able to develop resistance to them in the short term. The underlying structure of AMPs is critical in determining the selectivity with which they target their respective targets. As far as we know, peptides have not been tested in a lab to see if they can fight bacteria, fungus, and viruses in real life. In this paper, we develop an artificial neural network (ANN) using a back propagation neural network (BPNN) that enables optimal classification of tendency of a peptide sequence that involves the activities of antifungal, antibacterial, or antiviral. The BPNN is trained on the datasets collected across different repositories and then the overfitting is avoided using particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. Hence, at the time of testing, the BPNN clearly finds the predicted samples belonging to the same classes and this avoids the problem of finding the false positives. The simulation is conducted to test the efficacy of the model against various metrics that includes accuracy, precision, recall, and f1-measure. The effectiveness of the BPNN-PSO model in classifying instances at a faster rate than other techniques is demonstrated by its performance. The principle is straightforward, it is not difficult to programme, it converges more quickly, and it generally offers a superior solution.
Copyright © 2022 M. Rajkumar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Application of PSO-BPNN-PID Controller in Nutrient Solution EC Precise Control System: Applied Research.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 24;22(15):5515. doi: 10.3390/s22155515. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35898019 Free PMC article.
-
Research on Digital Economy of Intelligent Emergency Risk Avoidance in Sudden Financial Disasters Based on PSO-BPNN Algorithm.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021 Nov 30;2021:7708422. doi: 10.1155/2021/7708422. eCollection 2021. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021. Retraction in: Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9837251. doi: 10.1155/2023/9837251. PMID: 34887916 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Particle swarm algorithm trained neural network for QSAR studies of inhibitors of platelet-derived growth factor receptor phosphorylation.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006 Aug;28(5):369-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2006.04.001. Epub 2006 Apr 18. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006. PMID: 16713200
-
An Apple Fungal Infection Detection Model Based on BPNN Optimized by Sparrow Search Algorithm.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Aug 28;12(9):692. doi: 10.3390/bios12090692. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140077 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating Unusual Modes of Action and Resistance of Antibacterial Peptides.Curr Top Med Chem. 2017;17(5):520-536. doi: 10.2174/1568026616666160713123203. Curr Top Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27411328 Review.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Impact of ANN in Revealing of Viral Peptides.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Dec 29;2023:9835650. doi: 10.1155/2023/9835650. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 38188747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdollahzadeh E., Nematollahi A., Hosseini H. Composition of antimicrobial edible films and methods for assessing their antimicrobial activity: a review. Trends in Food Science & Technology . 2021;110:291–303. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.084. - DOI
-
- Makvandi P., Wang C. Y., Zare E. N., Borzacchiello A., Niu L. N., Tay F. R. Metal based nanomaterials in biomedical applications: antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity aspects. Advanced Functional Materials . 2020;30(22, article 1910021) doi: 10.1002/adfm.201910021. - DOI
-
- Lira M. H. P. D., Andrade Júnior F. P. D., Moraes G. F. Q., Macena G. D. S., Pereira F. D. O., Lima I. O. Antimicrobial activity of geraniol: an integrative review. Journal of Essential Oil Research . 2020;32(3):187–197. doi: 10.1080/10412905.2020.1745697. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous