Use of doppler ultrasound to predict need for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt revision
- PMID: 35978660
- PMCID: PMC9258261
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1200
Use of doppler ultrasound to predict need for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt revision
Abstract
Background: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is used to treat complications of portal hypertension, such as ascites and variceal bleeding (VB). While liver doppler ultrasound (DUS) is used to assess TIPS patency, trans-shunt venography (TSV) is the gold standard.
Aim: To determine the accuracy of DUS to assess TIPS dysfunction and for need for revision.
Methods: Retrospective review of patients referred for TIPS revision from 2008-2021. Demographics, DUS parameters at baseline and at the DUS preceding TIPS revision, TSV data were collected. Receiver operating characteristics curves, sensitivity, specificity, performance for doppler to predict need for revision were performed. Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to predict clinical factors associated with need for TIPS revision.
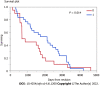
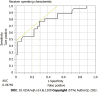
Results: The cohort consisted of 89 patients with cirrhosis (64% men, 76% white, 31% alcohol as etiology); median age 59 years. Indication for initial TIPS were VB (41%), refractory ascites (51%), and other (8%). TIPS was revised in 44%. On univariate analysis, factors associated with need for TIPS revision were male (P = 0.03), initial indication for TIPS (P = 0.05) and indication for revision (P = 0.01). Revision of TIPS was associated with lower mortality (26% vs 46%) and significantly lower rates of transplant (13% vs 24%; P = 0.1). In predicting need for TIPS revision, DUS has a 40% sensitivity, 45% specificity, PPV 78%, and NPV 14%. The most accurate location for shunt velocity measure was distal velocity (Area under the curve: 0.79; P = 0.0007).
Conclusion: DUS has poor overall sensitivity and specificity in predicting need for TIPS revision. Non-invasive methods of predicting TIPS dysfunction are needed since those needing TIPS revision had better survival.
Keywords: Doppler ultrasound; Portal hypertension; Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No conflicts of interest for all authors.
Figures
References
-
- Benito A. Doppler ultrasound for TIPS: does it work? Abdominal Imaging . 2004:45–52. - PubMed
-
- Brants L, Leiderman M, Veitsman E, Ofer A, Beck-Razi N. Role of Doppler Ultrasound Combined With Clinical Features in the Diagnosis of Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Dysfunction in the Era of Covered Stents. J Ultrasound Med. 2020;39:2373–2377. - PubMed
-
- Kanterman RY, Darcy MD, Middleton WD, Sterling KM, Teefey SA, Pilgram TK. Doppler sonography findings associated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt malfunction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997;168:467–472. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources