Sporadic Burkitt Lymphoma of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spinal Canal in an Adult: Oncogenicity and a Literature Review
- PMID: 35978743
- PMCID: PMC9375639
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.26860
Sporadic Burkitt Lymphoma of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spinal Canal in an Adult: Oncogenicity and a Literature Review
Abstract
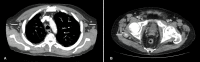
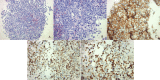
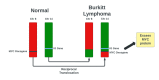
Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is an aggressive form of lymphoma that occurs due to translocation of the c-myc proto-oncogene on chromosome 8. BL is characterized by three distinct groups: African/endemic variant, immunosuppressive variant, or sporadic variant. Most cases of the sporadic variant occur in patients less than 40 years of age with a median age of 30 at diagnosis and are primarily seen in Caucasians. An immunocompetent 69-year-old male presented with subacute onset weakness in the lower extremities. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lumbar spine revealed a mass in the right paraspinal musculature with epidural extension, neural foraminal narrowing, and severe spinal canal stenosis in L2-L5. MRI of the thoracic spine revealed significant T5-T6 cord compression due to metastatic masses. Further diagnostic imaging revealed diffuse lymphadenopathy within the mediastinum and abdomen. Subsequently, the patient underwent a core needle biopsy of the left axillary lymph node, which revealed cluster of differentiation 20 and 10 (CD20 and CD10), c-myc, and B-cell lymphoma 6 (Bcl-6) positive lymphoid cells. A diagnosis of BL was made. The patient was treated with oral steroids and received one round of radiation therapy. The patient opted to forgo any antitumor treatment and was discharged to hospice. Primary lymphomas of the central nervous system (CNS) account for <5% of all CNS tumors. Approximately 5-10% of CNS lymphomas are recorded as BL, with the majority classified as high-grade B-cell lymphomas. Paraspinal involvement with BL is rare and not commonly seen in the sporadic variant.
Keywords: burkitt lymphoma; codox; epidural; ivac; neurology; oncology; radiology; spinal canal; spinal cord; sporadic burkitt lymphoma.
Copyright © 2022, Srichawla et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transformation of Follicular Lymphoma to a High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma With MYC and BCL2 Translocations and Overlapping Features of Burkitt Lymphoma and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Case Report and Literature Review.Clin Med Insights Blood Disord. 2017 Feb 28;10:1179545X17692544. doi: 10.1177/1179545X17692544. eCollection 2017. Clin Med Insights Blood Disord. 2017. PMID: 28579851 Free PMC article.
-
Burkitt leukaemia/lymphoma: R-CODOX-M/R-IVAC remains gold standard treatment in BL.Ir J Med Sci. 2016 Nov;185(4):773-777. doi: 10.1007/s11845-015-1288-3. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Ir J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 25843016
-
From the archives of MD Anderson Cancer Center: Sporadic Burkitt lymphoma with a complex karyotype and SOX11 expression.Ann Diagn Pathol. 2023 Oct;66:152182. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2023.152182. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37543028 Review.
-
Primary epidural sporadic Burkitt lymphoma in a 3-year-old: Case report and literature review.Surg Neurol Int. 2022 Mar 25;13:106. doi: 10.25259/SNI_1172_2021. eCollection 2022. Surg Neurol Int. 2022. PMID: 35399880 Free PMC article.
-
Translocations involving 8q24 in Burkitt lymphoma and other malignant lymphomas: a historical review of cytogenetics in the light of todays knowledge.Leukemia. 2009 Feb;23(2):225-34. doi: 10.1038/leu.2008.281. Epub 2008 Oct 16. Leukemia. 2009. PMID: 18923440 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
