Characteristics of inflammatory bowel diseases in patients with concurrent immune-mediated inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 35978883
- PMCID: PMC9280738
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i25.2843
Characteristics of inflammatory bowel diseases in patients with concurrent immune-mediated inflammatory diseases
Abstract
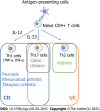
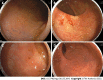
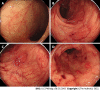
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are more likely to have concurrent immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) than those without IBD. IMIDs have been observed to alter the phenotype and outcomes of IBD in recent studies. Several studies have found that IBD patients with concurrent IMIDs may have more extensive or severe disease phenotypes, and are considered to be at increased risk of requiring biologics and IBD-related surgeries, suggesting that having multiple IMIDs is a poor prognostic factor for IBD. Furthermore, IBD patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis and Takayasu arteritis are reported to have unique endoscopic phenotypes, suggesting concurrent IMIDs can influence IBD phenotype with specific intestinal inflammatory distributions. In this review, we discuss the pathogenesis, disease phenotypes, and clinical outcomes in IBD patients with concomitant IMIDs.
Keywords: Concurrent immune-mediated inflammatory diseases; Inflammatory bowel disease; Outcomes; Phenotypes.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Akiyama S, Fukuda S, and Suzuki H have no relevant disclosures; Steinberg JM was on Advisory Board for Pfizer; Tsuchiya K has received grant supports from Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharmaceutical Corp., and Hitachi Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Ananthakrishnan AN, Bernstein CN, Iliopoulos D, Macpherson A, Neurath MF, Ali RAR, Vavricka SR, Fiocchi C. Environmental triggers in IBD: a review of progress and evidence. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:39–49. - PubMed
-
- Younis N, Zarif R, Mahfouz R. Inflammatory bowel disease: between genetics and microbiota. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47:3053–3063. - PubMed
-
- Anderson CA, Boucher G, Lees CW, Franke A, D'Amato M, Taylor KD, Lee JC, Goyette P, Imielinski M, Latiano A, Lagacé C, Scott R, Amininejad L, Bumpstead S, Baidoo L, Baldassano RN, Barclay M, Bayless TM, Brand S, Büning C, Colombel JF, Denson LA, De Vos M, Dubinsky M, Edwards C, Ellinghaus D, Fehrmann RS, Floyd JA, Florin T, Franchimont D, Franke L, Georges M, Glas J, Glazer NL, Guthery SL, Haritunians T, Hayward NK, Hugot JP, Jobin G, Laukens D, Lawrance I, Lémann M, Levine A, Libioulle C, Louis E, McGovern DP, Milla M, Montgomery GW, Morley KI, Mowat C, Ng A, Newman W, Ophoff RA, Papi L, Palmieri O, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Panés J, Phillips A, Prescott NJ, Proctor DD, Roberts R, Russell R, Rutgeerts P, Sanderson J, Sans M, Schumm P, Seibold F, Sharma Y, Simms LA, Seielstad M, Steinhart AH, Targan SR, van den Berg LH, Vatn M, Verspaget H, Walters T, Wijmenga C, Wilson DC, Westra HJ, Xavier RJ, Zhao ZZ, Ponsioen CY, Andersen V, Torkvist L, Gazouli M, Anagnou NP, Karlsen TH, Kupcinskas L, Sventoraityte J, Mansfield JC, Kugathasan S, Silverberg MS, Halfvarson J, Rotter JI, Mathew CG, Griffiths AM, Gearry R, Ahmad T, Brant SR, Chamaillard M, Satsangi J, Cho JH, Schreiber S, Daly MJ, Barrett JC, Parkes M, Annese V, Hakonarson H, Radford-Smith G, Duerr RH, Vermeire S, Weersma RK, Rioux JD. Meta-analysis identifies 29 additional ulcerative colitis risk loci, increasing the number of confirmed associations to 47. Nat Genet. 2011;43:246–252. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

