m6A-Related lncRNAs Predict Overall Survival of Patients and Regulate the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Osteosarcoma
- PMID: 35978902
- PMCID: PMC9377863
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9315283
m6A-Related lncRNAs Predict Overall Survival of Patients and Regulate the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Osteosarcoma
Abstract
Background: m6A-related lncRNAs have demonstrated great potential tumor diagnostic and therapeutic targets. The goal of this work was to find m6A-regulated lncRNAs in osteosarcoma patients.
Method: The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database was used to retrieve RNA sequencing and medical information from osteosarcoma sufferers. The Pearson's correlation test was used to identify the m6A-related lncRNAs. A risk model was built using univariate and multivariable Cox regression analysis. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and receiver functional requirements were used to assess the risk model's performance (ROC). By using the CIBERSORT method, the associations between the relative risks and different immune cell infiltration were investigated. Lastly, the bioactivities of high-risk and low-risk subgroups were investigated using Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA).
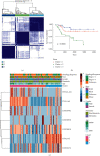
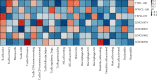
Result: A total of 531 m6A-related lncRNAs were obtained from TCGA. Seven lncRNAs have demonstrated prognostic values. A total of 88 OS patients were separated into cluster 1, cluster 2, and cluster 3. The overall survival rate of OS patients in cluster 3 was more favorable than that of those in cluster 1 and cluster 2. The average Stromal score was much higher in cluster 1 than in cluster 2 and cluster 3 (P < 0.05). The expression levels of lncRNAs used in the construction of the risk prediction model in the high-risk group were generally lower than those in the low-risk group. Analysis of patient survival indicated that the survival of the low-risk group was higher than that of the high-risk group (P < 0.0001) and the area under the curve (AUC) of the ROC curve was 0.719. Using the CIBERSORT algorithm, the results revealed that Macrophages M0, Macrophages M2, and T cells CD4 memory resting accounted for a large proportion of immune cell infiltration. By GSEA analysis, our results implied that the high-risk group was mainly involved in unfolded protein response, DNA repair signaling, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling pathway and glycolysis pathway; meanwhile, the low-risk group was mainly involved in estrogen response early and KRAS signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Our investigation showed that m6A-related lncRNAs remained tightly connected to the immunological microenvironment of osteosarcoma tumors, potentially influencing carcinogenesis and development. The immune microenvironment and immune-related biochemical pathways can be changed by regulating the transcription of M6A modulators or lncRNAs. In addition, we looked for risk-related signaling of m6A-related lncRNAs in osteosarcomas and built and validated the risk prediction system. The findings of our current analysis will facilitate the assessment of outcomes and the development of immunotherapies for sufferers of osteosarcomas.
Copyright © 2022 Yikang Bi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of tumor immune microenvironment and prognosis of m6A-related lncRNAs in gastric cancer.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 24;22(1):316. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09377-8. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35331183 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methylandenosine-related lncRNAs play an important role in the prognosis and immune microenvironment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 8;11(1):17844. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97362-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34497315 Free PMC article.
-
N6-Methyladenosine-Related LncRNAs Are Potential Remodeling Indicators in the Tumor Microenvironment and Prognostic Markers in Osteosarcoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 12;12:806189. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.806189. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095893 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insight into the functions of N6‑methyladenosine modified lncRNAs in cancers (Review).Int J Oncol. 2022 Dec;61(6):152. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5442. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Int J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36263625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of lncRNAs in the tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy of melanoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 19;13:1085766. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1085766. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36601121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unlocking the tumor-immune microenvironment in osteosarcoma: insights into the immune landscape and mechanisms.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 18;15:1394284. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1394284. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39359731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in osteosarcoma: expression, function and interaction with noncoding RNAs - an updated review.Epigenetics. 2023 Dec;18(1):2260213. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2023.2260213. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Epigenetics. 2023. PMID: 37766615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances of m6A methylation in skeletal system disease.J Transl Med. 2024 Feb 14;22(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04944-y. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38355483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Modulation of Estrogen Receptor Signaling in Ovarian Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 28;26(1):166. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010166. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39796024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNA-Mediated N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) deposition: A pivotal regulator of cancer, impacting key signaling pathways in carcinogenesis and therapy response.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 Nov 13;9(1):84-104. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.11.005. eCollection 2024 Mar. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 38075202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

