Traditional Chinese Medicine Formula Jian Pi Tiao Gan Yin Reduces Obesity in Mice by Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolism
- PMID: 35979004
- PMCID: PMC9377893
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9727889
Traditional Chinese Medicine Formula Jian Pi Tiao Gan Yin Reduces Obesity in Mice by Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolism
Abstract
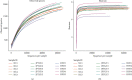
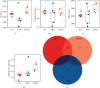
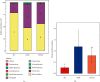
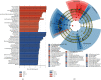
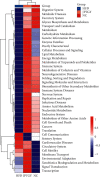
The current study employed the high-fat diet (HFD) induced murine model to assess the relationship between the effect of Jian Pi Tiao Gan Yin (JPTGY) and the alterations of gut microbiota and fecal metabolism. C57BL/6 mice were used to establish an animal model of obesity via HFD induce. Serum biochemical indicators of lipid metabolism were used to evaluate the pharmacodynamics of JPTGY in obese mice. Bacterial communities and metabolites in the feces specimens from the controls, the Group HFD, and the JPTGY-exposed corpulency group were studied by 16s rDNA genetic sequence in combination with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) based untargeted fecal metabolomics techniques. Results revealed that JPTGY significantly decreased the levels of total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and elevated high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). Moreover, JPTGY could up-regulate the abundance and diversity of fecal microbiota, which was characterized by the higher phylum of proteobacteria. Consistently, at the genus levels, JPTGY supplementation induced enrichments in Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group, Oscillibacter, Turicibacter, Clostridium sensu stricto 1, and Intestinimonas, which were intimately related to 14 pivotal fecal metabolins in respond to JPTGY therapy were determined. What is more, metabolomics further analyses show that the therapeutic effect of JPTGY for obesity involves linoleic acid (LA) metabolism paths, alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) metabolism paths, glycerophospholipid metabolism paths, arachidonic acid (AA) metabolism paths, and pyrimidine metabolism paths, which implied the potential mechanism of JPTGY in treating obesity. It was concluded that the linking of corpulency phenotypes with intestinal flora and fecal metabolins unveils the latent causal link of JPTGY in the treatment of hyperlipidemia and obesity.
Copyright © 2022 Wenchao Dong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

