Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control rates of hypertension in patients hospitalized with atrial fibrillation in China: Findings from the CCC-AF project
- PMID: 35979022
- PMCID: PMC9376459
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.970787
Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control rates of hypertension in patients hospitalized with atrial fibrillation in China: Findings from the CCC-AF project
Abstract
Background: The status of hypertension in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) remains unknown in China.
Methods: This study used data from patients hospitalized with AF recruited by the Improving Care for Cardiovascular Disease in China-AF (CCC-AF) project from 236 hospitals enrolled by geographic-economic level in China from 2015 to 2019. The prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control rates of hypertension in patients hospitalized with AF were estimated. Multivariable logistic regression was used to analyze the factors associated with uncontrolled hypertension.
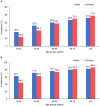
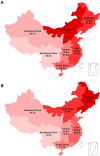
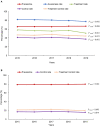
Results: Among 60,390 patients hospitalized with AF, the prevalence of hypertension according to the 2018 Chinese hypertension guidelines was 66.1%. The awareness, treatment, and control rates of hypertension were 80.3, 55.8, and 39.9%, respectively. Among patients treated for hypertension, the treatment control rate was 46.2%. These rates varied according to patient clinical characteristics and geographic regions. The young (18-44 and 45-54 years old), rural insurance, alcohol drinking, history of heart failure, valvular AF, first diagnosed AF, and permanent AF, were associated with uncontrolled hypertension. Under the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) hypertension guidelines, the prevalence of hypertension was 79.3%, and the control and treatment control rates dropped to 16.7 and 21.2%, respectively.
Conclusion: Hypertension is common in patients hospitalized with AF in China. Although most patients were aware of their hypertensive status, the treatment and control rates of hypertension were still low. The management of hypertension in patients with AF needs to be further improved.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; awareness; control; hypertension; prevalence; treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Sun, Hao, Liu, Yang, Qi, Hu, Yang, Wang, Zhao, Sang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Current status of thromboembolism risk assessment in patients hospitalized with non-valvular atrial fibrillation in tertiary hospitals in China].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2021 Sep 24;49(9):856-865. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20201231-01028. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34530592 Chinese.
-
Rationale and design of the improving Care for Cardiovascular Disease in China (CCC) project: a national registry to improve management of atrial fibrillation.BMJ Open. 2018 Jul 5;8(7):e020968. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020968. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 29980544 Free PMC article.
-
Atrial fibrillation prevalence, awareness and management in a nationwide survey of adults in China.Heart. 2021 Jan 28;107(7):535-41. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2020-317915. Online ahead of print. Heart. 2021. PMID: 33509976 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac pacing device therapy for atrial dysrhythmias: how does it work?AACN Clin Issues. 2004 Jul-Sep;15(3):377-90. doi: 10.1097/00044067-200407000-00006. AACN Clin Issues. 2004. PMID: 15475812 Review.
-
Increased Risk of Hypertension in Young Adults in Southwest China: Impact of the 2017 ACC/AHA High Blood Pressure Guideline.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2019 Feb 28;21(3):21. doi: 10.1007/s11906-019-0926-y. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2019. PMID: 30820764 Review.
Cited by
-
2023 Guideline for the management of hypertension in the elderly population in China.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2024 Jun 28;21(6):589-630. doi: 10.26599/1671-5411.2024.06.001. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38973827 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Vermond RA, Geelhoed B, Verweij N, Tieleman RG, Van der Harst P, Hillege HL, et al. . Incidence of atrial fibrillation and relationship with cardiovascular events, heart failure, and mortality: a community-based study from the Netherlands. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2015) 66:1000–7. 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.06.1314 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

